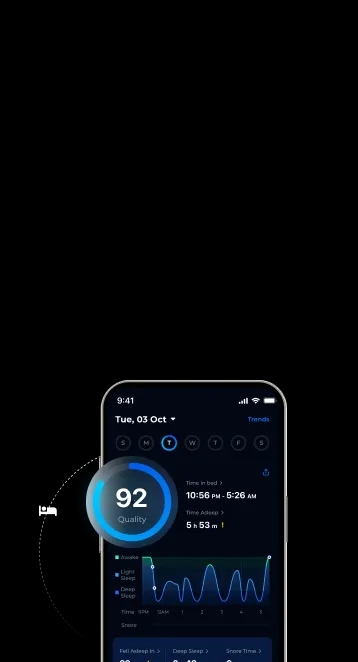


Do you ever wonder how long you can go without sleep? If you’re constantly swarmed with deadlines, you may feel pressure to sacrifice sleep to meet them. But when does this become too harmful?
In this article, we’ll explore the effects of sleep deprivation and how long you can go without sleep before it leads to dire health consequences.
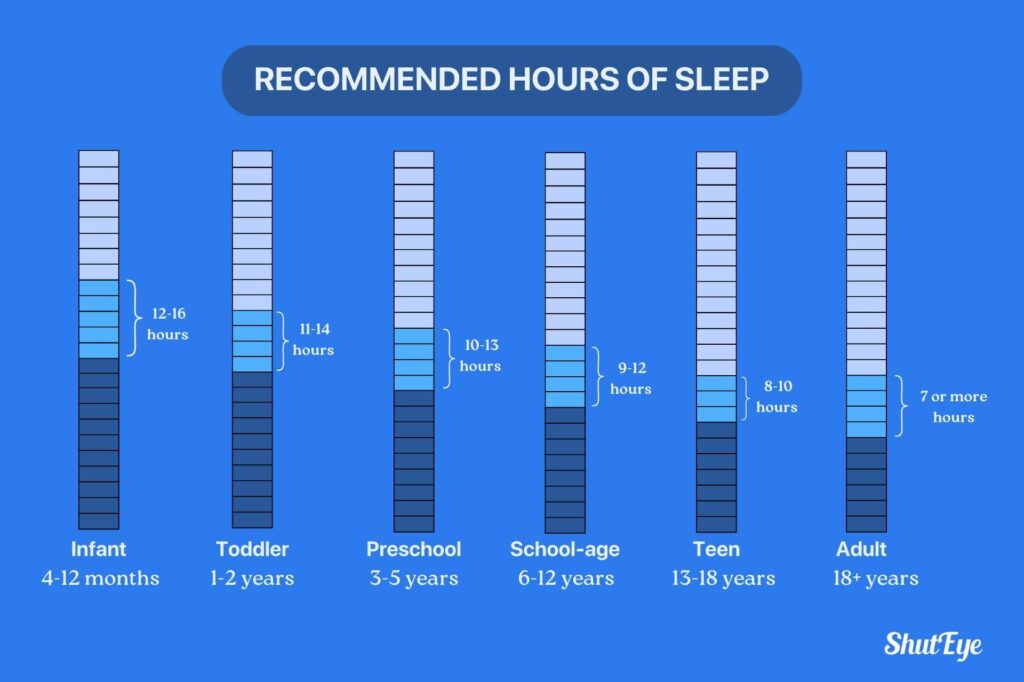
The amount of sleep that we need in a day, varies from person to person. Generally, experts recommend that adults should get between 7 to 9 hours of sleep each night while children should get between 8 to 16 hours of sleep each night, depending on age [1].
However, these are only general recommendations and not strict rules to follow. We should also consider sleep quality.
Sleep quality is about how well we sleep and whether we wake up frequently in the middle of the night. Poor quality sleep may affect our sleep duration and contribute to a lack of sleep.

According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), about a third of Americans do not get enough sleep at night [2]. When you get insufficient sleep, this leads to a condition called sleep deprivation.
Sleep deprivation is when you have an inadequate duration or quality of sleep to support your overall health and well-being [3]. In some cases, lack of sleep can be attributed to sleep disorders such as insomnia or obstructive sleep apnea.
Being sleep-deprived may lead to issues such as forgetfulness, poor physical and mental performance, irritability, anxiety, depression, a higher risk of developing heart disease and obesity, and an increased risk of high blood pressure and diabetes [4].
It’s a serious health issue that can lead to negative health consequences if it is not treated.
The effects of not getting enough restful sleep can set in as early as 24 hours with symptoms such as irritability or memory issues kicking in even before [5].
Here’s what you can expect to experience if you go 24 hours, 36 hours, 48 hours, and 72 hours without sleep:
It is not unusual for some people to pull an all-nighter especially if they are shift workers, have work to catch up on, have an exam to prepare for, or if you have a newborn at home.
Research suggests that going without sleep for more than 24 hours can cause you to have a performance similar to someone who has consumed alcohol up to 0.1% blood alcohol concentration (BAC) levels.
Additionally, some symptoms that you may experience are [6]:
Extending the period of acute sleep deprivation to 36 hours leads to more severe and noticeable effects, impacting your physical and mental health.
Here are some of the side effects [7], [8]:
Past the 48-hour mark is known as severe sleep deprivation. This is when your overall physical and mental performance starts to break down.
The side effects of prolonged sleep deprivation are [9]:
72 hours of sleep loss is considered to be extreme sleep deprivation. There are profound effects on the mind and body as a whole.
A study involving twelve male astronauts revealed that 72 hours of sleep deprivation led to significant cognitive impairment and a noticeable decline in positive emotions [10].
Some severe consequences of having no sleep for three days include [11]:

Based on the various side effects above, it can be said that the impact of sleep deprivation extends far beyond mere tiredness. It affects health both in the short term and long term.
Let’s compare some of the main consequences of short-term and long-term sleep deprivation [12]:
| Short Term Sleep Deprivation | Long Term Sleep Deprivation |
| Increased stress response | Increased blood pressure and risk of hypertension |
| Somatic problems | Impaired insulin sensitivity |
| Lower quality of life | Weight gain |
| Emotional distress | Increased risk of cancer |
| Mood disorders | Increased risk of anxiety, depression, and other mood disorders |
| Mental health-related issues | Long-term memory issues |
| Cognitive impairment | Hormone imbalances |
Understanding these consequences is crucial, as even a single night of insufficient sleep can trigger a cascade of negative effects on physical, mental, and emotional well-being.
See also: Can You Die From Lack of Sleep?
To understand your individual sleep needs, you must recognize that there’s no one-size-fits-all solution for how much sleep you need. Your amount of sleep needed can vary based on several factors, such as genetics and age. So, how do you determine your optimal sleep duration?
Here are a few key factors to consider:
Alternatively, you may determine the optimal sleep duration that you need by using ShutEye®’s free sleep calculator.


Now that you know the negative side effects of sleep deprivation, it’s important to ensure that you are taking the right steps towards good quality sleep. The best way to do so is to start making good sleep habits and sticking to them.
Here are some tips on how you can maintain healthy sleep habits:
Lack of sleep is not just about feeling fatigue or drowsiness. It can lead to a wide range of negative health consequences such as hallucinations, mood swings, poor performance, and increased risk of chronic conditions. It’s important to prioritize good sleep quality to prevent these effects.
To improve your sleep quality, try out the ShutEye® app. ShutEye® is a patented sleep-tracking app that tracks your sleep cycle and offers personalized sleep tips to combat sleep loss.
Amin F, Sankari A. Sleep Insufficiency. (2023). In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-. Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK585109/
CDC (2024) Sleep [online]. Available at: https://www.cdc.gov/cdi/indicator-definitions/sleep.html
Harrison, Y., & Horne, J. (1999). One Night of Sleep Loss Impairs Innovative Thinking and Flexible Decision Making. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 78(2), 128-145. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1006/obhd.1999.2827
John Hopkins Medicine (2024) The Effects of Sleep Deprivation [online]. Available at: https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/wellness-and-prevention/the-effects-of-sleep-deprivation
Liu, Q., Zhou, R., Liu, L., & Zhao, X. (2015). Effects of 72hours total sleep deprivation on male astronauts' executive functions and emotion. Comprehensive psychiatry, 61, 28–35. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comppsych.2015.05.015
Medic G, Wille M, Hemels ME. Short- and long-term health consequences of sleep disruption. Nat Sci Sleep. 2017 May 19;9:151-161. doi: 10.2147/NSS.S134864. PMID: 28579842; PMCID: PMC5449130.
National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute (2022) How Much Sleep Is Enough? [online]. Available at: https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/sleep/how-much-sleep
National Council on Aging (2024) Sleep Deprivation: Definition, Side Effects, and Treatment [online]. Available at: https://www.ncoa.org/adviser/sleep/sleep-deprivation/
Paillard, T. (2023). Detrimental effects of sleep deprivation on the regulatory mechanisms of postural balance: A comprehensive review. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 17, 1146550. Available at: https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2023.1146550
Waters, F., Chiu, V., Atkinson, A., & Blom, J. D. (2018). Severe Sleep Deprivation Causes Hallucinations and a Gradual Progression Toward Psychosis With Increasing Time Awake. Frontiers in Psychiatry, 9, 350067. Available at: https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2018.00303
Williamson AM, Feyer AM. Moderate sleep deprivation produces impairments in cognitive and motor performance equivalent to legally prescribed levels of alcohol intoxication. Occup Environ Med. 2000 Oct;57(10):649-55. doi: 10.1136/oem.57.10.649. PMID: 10984335; PMCID: PMC1739867.