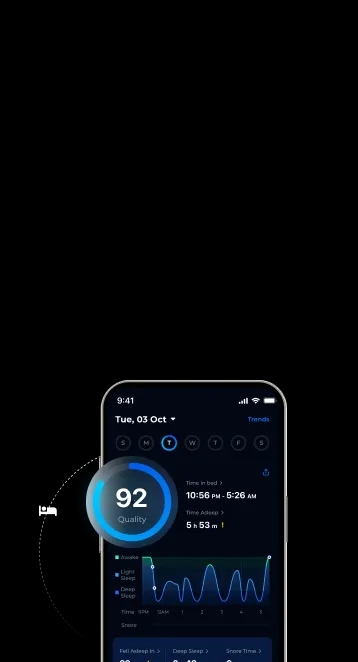


It is normal for us to experience some stress and anxiety in our daily lives from external stressors such as our jobs, personal commitments, or mental health challenges. But when we continue to feel this way even at night, it can severely impact our sleep quality. How to sleep when you’re feeling stressed and anxious? Keep reading to find out practical tips and tricks.
Anxiety is defined as a feeling of fear, dread, or restlessness. It is a normal reaction that we may have to distressing or stressful situations. However, if this fear persists for months and gets worse over time, it’s likely to be a form of anxiety disorder [1].
Besides fear or dread, some common symptoms of anxiety disorders include [2]:
Sleep and mood are highly interconnected. If we are in a poor mood, it can affect our ability to sleep. If we have sleep difficulties and sleep deprivation, it can affect our mood and mental health.
Stress can affect our sleep quality in many ways. When we are stressed, our cortisol level rises causing a heightened arousal, and sleep disruption. This hormonal imbalance will result in a much lighter and less restorative sleep [3].
Likewise, anxiety may also disrupt sleep as it causes feelings of agitation and arousal [4].

Sleep is an essential process that we cannot live without. It helps to restore our brain function, process information for learning, and consolidate memories so that we can function properly during the daytime.
Poor sleep or sleep disorders like insomnia are associated with a variety of mental health difficulties such as fatigue, poor concentration, increased negative emotions, and memory lapses [5], [6].
Additionally, it increases the risk of mental health disorders such as anxiety disorders and depression. Getting good quality sleep will help to reduce these problems and enhance mood regulation for better health overall.
If you are facing sleep problems due to anxiety disorders, depression, or mental health-related issues, the first step may be for you to look into your sleep habits. It could be a matter of practicing good sleep hygiene to improve the overall quality of your sleep.
Here are some practical tips to help you sleep when stressed or anxious:
Having a soothing bedtime routine can help to signal the body when it’s time to sleep. Some activities that you can do to relax the mind include reading a bedtime story, taking a warm bath, meditating, or practicing deep breathing.
Try to avoid activities that may be stressful or stimulating. It’s also best to avoid electronic devices and blue light an hour before going to bed so that melatonin production does not get interrupted.
Maintaining a regular sleep and wake-up schedule, even on the weekend can help to regulate the body’s internal clock. Doing this all the time will make it easier for you to fall asleep and wake up in the mornings.

Your sleep environment can also have an impact on your sleep quality. Your room should be kept dark, quiet, and cool for a comfortable sleep experience. This can be achieved by using blackout curtains, white noise machine,e or ensuring that you have a comfortable mattress. Ensure that your bedroom is set at a temperature that’s cool (between 60-75ºF).

Caffeine is a stimulant that can keep you awake for hours, so taking it before bedtime or too late in the day is not advisable. If you’re a coffee lover, you want to make sure that you are consuming it in the morning or at least 4 to 6 hours before bed.
On the other hand, while alcohol may induce drowsiness initially, it can turn into a stimulant and disrupt sleep cycles later at night. It is best to limit your alcohol intake to 1 to 2 cups a day and ensure that you are not taking it when it’s close to bedtime.
Eating large and heavy meals just before bedtime can potentially disrupt your sleep throughout the night. Our bodies generally need 2 to 3 hours to digest the food that we eat. So, going to sleep after eating may result in incomplete digestion and cause discomfort or acid reflux.
It is best to consume any large or heavy meals at least 2 to 3 hours before going to sleep. If you still feel hungry, you may opt for light snacks such as yogurt or a banana.
Tossing and turning in bed and trying to force yourself to sleep will only increase feelings of frustration and anxiety. If you find yourself not being able to sleep even after 20 minutes of being in bed, it’s time to get out of bed. Instead, try doing a soothing activity like stretching, reading a book, or listening to music until you feel tired enough to fall asleep.
You want to make sure that your mind associates the idea of your bed with sleep and rest. That way, when you lie down at night, your body naturally starts to feel sleepy instead of staying alert or restless.
You should seek professional help if the feelings of stress and anxiety start to feel overwhelming to the point where it is significantly affecting your daily life, and personal or professional relationships, causing persistent sleep problems or withdrawal from activities that you used to enjoy.
You should also seek professional help if you are experiencing nocturnal panic attacks, nighttime anxiety, or extreme fear. From there, your doctor will be able to properly advise you on the next course of action and if there is a need for cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) or medications to help you fall asleep faster.
It is possible to fall asleep even when you feel stressed or anxious. By prioritizing good sleep hygiene practices—such as creating a relaxing environment, establishing a consistent sleep schedule, and practicing mindfulness techniques—you can improve your sleep quality and overall well-being.
Still, struggling to silence the loud thoughts in your mind? You may want to consider using the ShutEye® app. With soothing sleep sounds, guided meditations, and personalized sleep tracking, you’ll have the tools you need to relax and fall asleep faster. Try today for FREE!
Compassion Behavioral Health (2024) The Link Between Anxiety Disorder and Sleep Problems [online]. Available at: https://compassionbehavioralhealth.com/the-link-between-anxiety-disorder-and-sleep-problems/
Division of Sleep Medicine Harvard Medical School (2021) Sleep and Mood [online]. Available at: https://sleep.hms.harvard.edu/education-training/public-education/sleep-and-health-education-program/sleep-health-education-87
MedlinePlus (2023) Anxiety [online]. Available at: https://medlineplus.gov/anxiety.html
Mental Health Foundation (2025) Sleep Matters: The Impact Of Sleep On Health And Wellbeing [online]. Available at: https://www.mentalhealth.org.uk/explore-mental-health/publications/sleep-matters-impact-sleep-health-and-wellbeing
Scott, A. J., Webb, T. L., Martyn-St James, M., Rowse, G., & Weich, S. (2021) Improving sleep quality leads to better mental health: A meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Sleep Medicine Reviews, 60, 101556 [online]. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smrv.2021.101556
World Health Organization (2023) Anxiety disorders [online]. Available at: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/anxiety-disorders