

When you try to rush to meet a work deadline or cram for an exam, you’ll probably stay up all night for it without thinking much of the consequences. But did you know that when you do this, you face the risk of sleep deprivation? Going 48 hours, no sleep and longer can lead to negative health consequences.
In this article, we’ll discover the different effects of not sleeping for more than a day and strategies to recover from lack of sleep.

The short answer is— no, it is not okay. Going without sleep for extended periods will lead you to experience a condition called sleep deprivation. It is detrimental to both your body and mind as it can cause cognitive impairment. You may also experience brief episodes of unconsciousness, known as microsleep [1].
It is recommended for normal, healthy adults to get between seven to nine hours of sleep each night. However, this number may change depending on individual sleep needs.
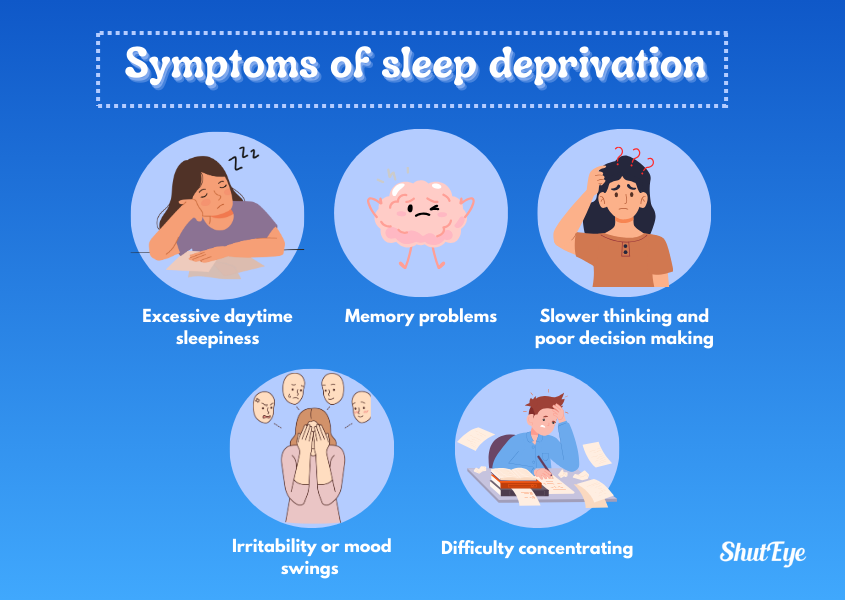
Not getting enough sleep can lead to sleep loss, also known as sleep deprivation [2]. Being sleep-deprived can lead to several health conditions or issues, including:
The first stage of sleep deprivation kicks in after 24 hours of no sleep. This is when you’ll start to feel tired or drained. Your alertness and attention span will start to decrease, making you more prone to committing mistakes in simple, everyday tasks.
Additionally, studies also discovered similarities between cognitive and physiological impairment due to fatigue and impairment due to alcohol consumption. It is suggested that going 24 hours without sleep is similar to having a blood alcohol content level of 0.10%, past the legal limit in the United States [3].
Your stress hormones will also likely increase during this stage to cope with the fatigue and help you to continue functioning.
After 36 hours of not sleeping, the effects will start to increase in severity. These extended hours without sleep come with alarming effects on both your physical health and mental health. You may experience physical symptoms such as a strong urge to sleep, extreme fatigue, and hunger. You may also experience hallucinations and microsleep episodes.
Past 48 hours without sleep, it becomes known as extreme sleep deprivation. It will be hard for you to even keep your eyes open and at the same time, you may experience other effects like:
Your risk for diabetes and chronic diseases will also increase at this point.
After reaching the 72-hour mark, the desire to sleep is almost unbearable. Microsleeps are longer and more frequent. Your perception of the world around you starts to warp. Your emotions might be all over the place. You could feel irritable, anxious, or even depressed.
Worst of all, you may see complex hallucinations, have delusions, or experience disordered thinking.
At this point, recovering from sleep deprivation will be a long process. Even if you prioritize sleeping about 7 to 8 hours per night, you may wake up groggy the next day. It might take weeks for your body to recover.
If you push through to 96 hours or more without sleep, you’ve officially reached dangerous territory. Your perception of reality can become severely warped, and the need for sleep will become nearly overpowering.
In some cases, you might even experience sleep deprivation psychosis, making it hard to tell what’s real. Not only that, but chronic poor sleep can lead to an increased risk for serious health issues like hypertension, heart attack, stroke, diabetes, dementia, and even certain cancers [4].
The good news is that these effects are reversible provided that you prioritize getting enough restful sleep. However, it may take a while to recover from long-term sleep deprivation. So, before you decide to sacrifice sleep in favor of work, think twice about the potential consequences.
The time that it takes to recover from sleep deprivation really depends on how long you have stayed awake. For example, getting 30% less sleep than your body needs for a few days may require more than a week’s worth of proper sleep to recover [5].
Research suggests that even if it is acute sleep deprivation, it may take a longer time than expected to fully recover [6].
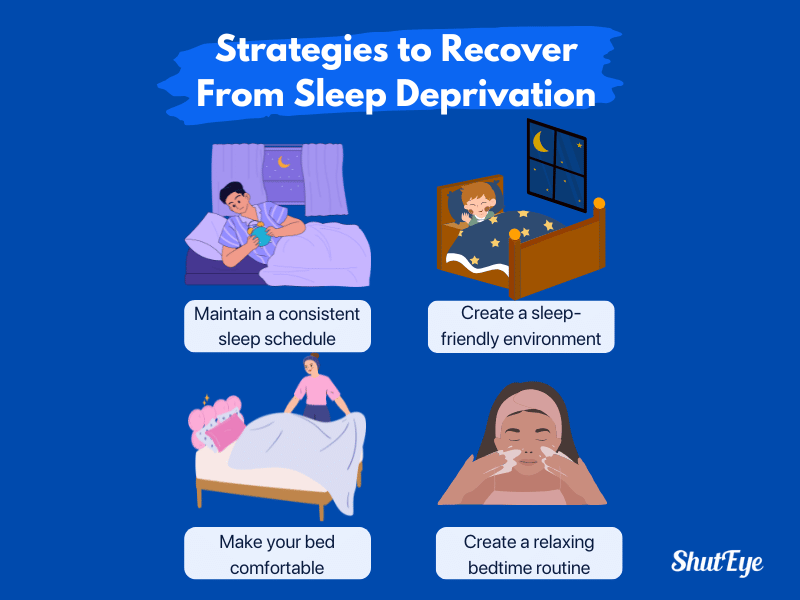
Sleep deprivation impairs the accurate recognition of human emotions and leads to numerous other issues that can lower your quality of life. A simple yet effective way to recover is to ensure you get enough quality sleep.
Here are some strategies that can help you bounce back, fall asleep faster, and improve sleep quality:
If not being able to sleep starts to affect your quality of life, you may want to consider consulting with a doctor for medical advice and proper diagnosis. Seeking professional help can help you to rule out or identify if your sleep deprivation is caused by underlying sleep disorders such as obstructive sleep apnea, insomnia, restless leg syndrome (RLS), or others.
Going without sleep for 48 hours can have severe effects on both your physical and mental well-being. From impaired cognitive performance to extreme fatigue and disordered thinking, sleep deprivation can have severe consequences. Preventing sleep deprivation requires you to practice good sleep habits.
One way to help you keep track of your sleep habits is by using the ShutEye® app. ShutEye monitors your sleep patterns and provides you with a detailed report of how your night went. Based on this, you’ll receive personalized recommendations to help you improve your habits for a good night’s rest. Try it for free, limited time only!
Biggers, A. (2019) The effects of going more than 24 hours without sleep [online]. Available at: https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/324799
Centre for Disease Prevention (2020) NIOSH Training for Nurses on Shift Work and Long Work Hours [online]. Available at: https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/work-hour-training-for-nurses/longhours/mod3/08.html
John Hopkins Medicine (2025) Health Risks of Poor Sleep [online]. Available at: https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/wellness-and-prevention/health-risks-of-poor-sleep
John Hopkins Medicine (2025) Sleep Deprivation [online]. Available at: https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/sleep-deprivation
Kiefer, D. (2021) Recovering from sleep deprivation takes longer than expected [online]. Available at: https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/recovering-from-sleep-deprivation-takes-longer-than-expected
LaMotte, S. (2021) Recovering from a lack of sleep takes longer than you might think, study says [online]. Available at: https://edition.cnn.com/2021/09/09/health/sleep-deficit-recovery-wellness/index.html