

Whether you find yourself dozing off sprawled out on your back or comfortably curled up in a ball, the way you position yourself during sleep significantly influences the quality of your sleep. Understanding your body becomes crucial in determining the best sleeping position.
Especially if you struggle with back pain, heart conditions, snoring, sleep apnea, or wrinkles, choosing the right sleeping position can make a world of difference!
Among different types of sleeping positions, there are side, back, fetal and stomach sleepers.
However, experts say sleeping on the side or back is more beneficial than sleeping on the stomach. According to the study, side sleeping is the most common sleep position – approximately 74%! A side sleeper sleeps on the left or right side of their body. They often prefer fetal position as they find confort in this position.
Discover in the next paragraphs specifics about all the sleeping positions and learn how they affect health.
Back sleeping, also known as the supine position, is characterized by lying on your back, which relaxes all back muscles and maintains a natural neck position. There are two common variations of back position:
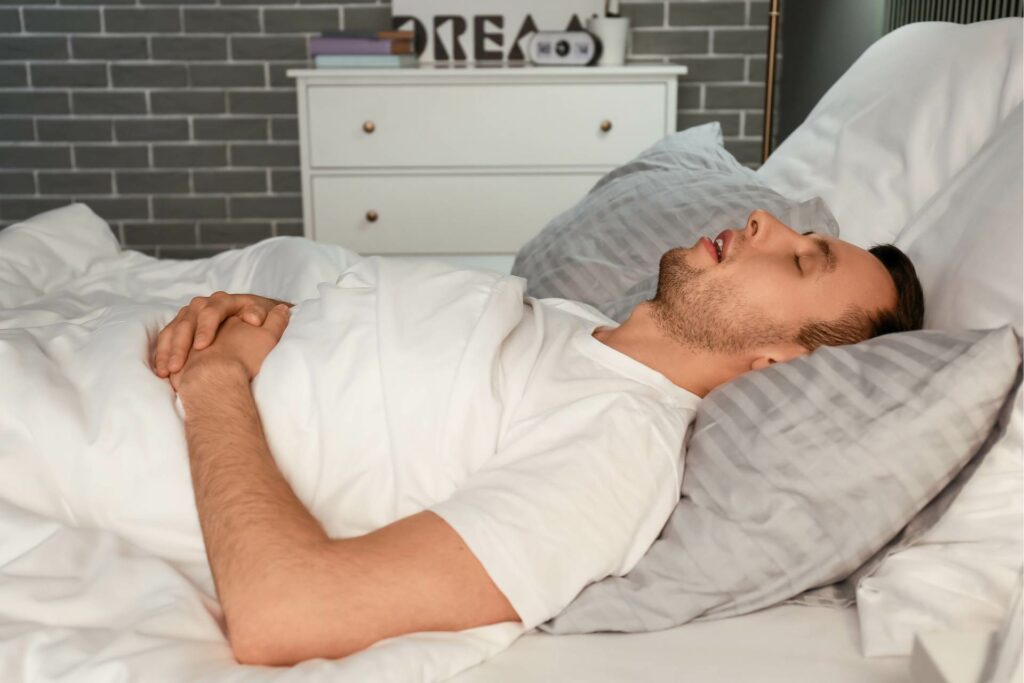

To ensure the best neck posture, opt for a comfortable pillow with a height of about a fist’s length. However, it’s crucial to note that gravity, pushing the tongue backward, can lead to poor ventilation, potentially promoting snoring. Despite this drawback, considering the numerous advantages and benefits for both sleep quality and overall health, back sleeping remains a highly recommended position. Discover why back sleeping stands out as one of the optimal choices for a good night’s sleep.
When it comes to finding relief from lower back pain, one option you can consider is sleeping on your back. Back sleeping, also known as a supine position, can help alleviate pressure on your lower back and provide relief from discomfort. By lying flat on your back, you can maintain a neutral spine position, which can help reduce strain on the muscles and joints in your lower back.

Sleeping on your back allows your spine to maintain its natural alignment. It can reduce the risk of back and neck pain. This position evenly distributes your body weight, preventing pressure points. It promotes a more comfortable sleep.
Back sleeping can help prevent skin irritation and wrinkles caused by contact with the pillow. Unlike side sleeping or stomach sleeping, which can cause friction and pressure on the face, sleeping on your back allows your skin to remain in a neutral position, minimizing the development of wrinkles.
Sleeping on the back facilitates the expansion of your airways, easing the process of breathing and decreasing the chances of snoring. Back sleeping also acts as a preventive measure against the collapse of soft tissues in the throat, a factor often linked to snoring and sleep apnea.
Sleeping on the side offers several benefits for improving your sleep quality. When you sleep on your side, you can experience improved back alignment. Additionally, people who sleep on their side can alleviate back and neck pain by reducing pressure on their spine. Side sleeping also aids in digestion and can reduce snoring. Pregnant women can benefit from sleeping on her left side as it improves circulation and reduces pressure on the vein carrying blood to the heart.
Side sleeping is the most common occurrence, and it is also one of the healthiest sleeping positions. However, it is interesting to note which side a sleeper should use for sound sleep. One might think it does not matter at all. However, some medical practitioners and researchers have explored the different benefits of sleeping on each side. Let us find it out here.
Sleeping on the left side can benefit many people in various conditions. Let us take a closer look at these scenarios:
The left-side sleeping is highly recommended for pregnant ladies. This sleeping position offers several benefits for both you and your baby.
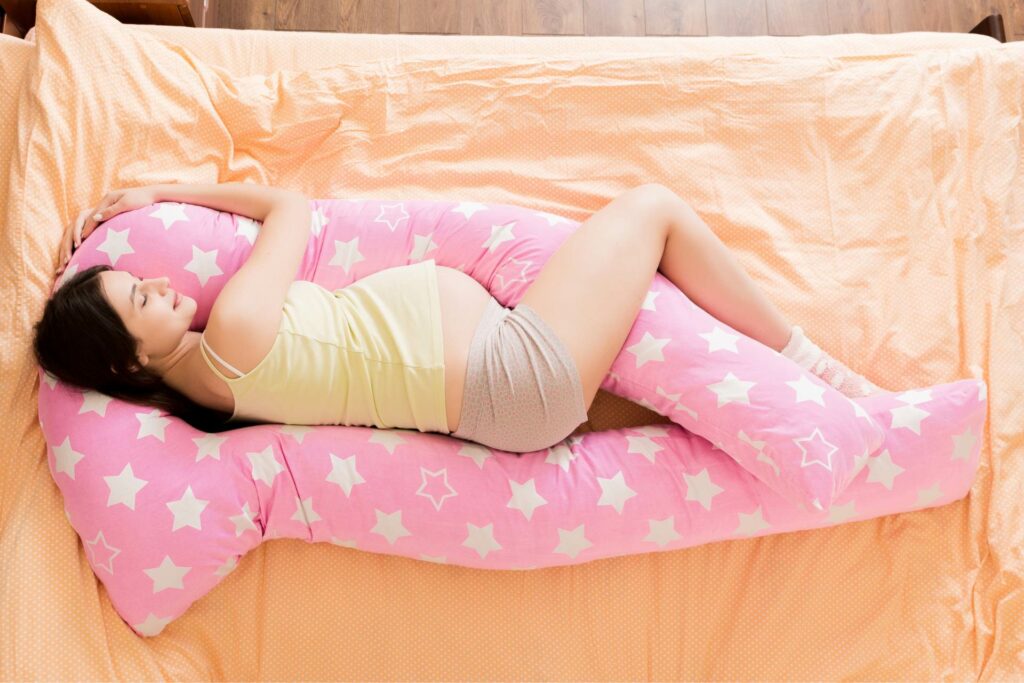

Here are four reasons why sleeping on their side is the best sleep position for pregnant women:
Remember to use extra pillows and blankets for added comfort and support. If your left side becomes uncomfortable, it’s okay to switch temporarily to the right side.
If you suffer from acid reflux and stomach aches, lying down right after a meal may not be healthy. Due to the stomach’s shape and the angle of its connection to the esophagus, it is also unwise to rest flat on your back. Therefore, for best health outcomes, doctors recommend left-side sleeping, which limits the amount of stomach acid exposed to the esophagus.

Sleeping on your left side can naturally open the airways to smooth your breathing process. You may also find relief if you rest on your right side. However, doctors consider sleeping on your left side to be more effective. Moreover, it is also the recommended sleeping position for individuals having sleep apnea.
According to research, people sleeping on their backs (instead of their sides) tend to snore more. It is because when you sleep on your back, your tongue falls back into your throat due to gravity. Consequently, it creates an obstruction that can result in snoring.
Blood vessels are located on the right side of the body. Therefore, researchers believe sleeping on the left side can relieve pressure and help people with high blood pressure.
As our bodies are not symmetrical, sleeping on the left side is unsuitable for everyone. Therefore, one group of people can benefit from sleeping on their right side.
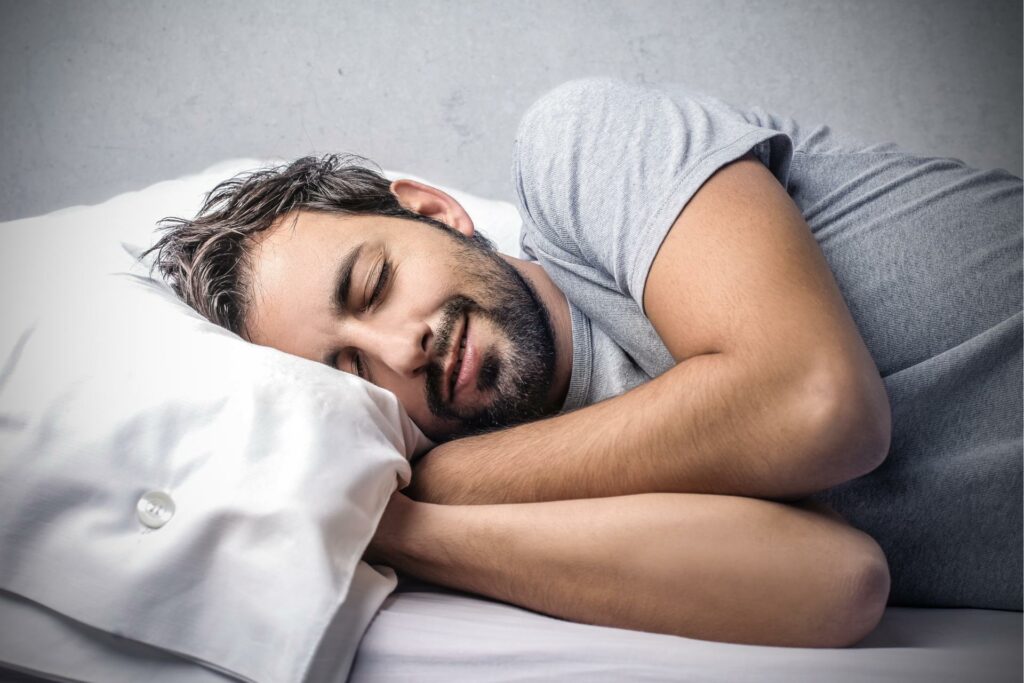

People with heart failure should also avoid sleeping on their backs since it puts pressure on the lungs and may contribute to sleep apnea symptoms. According to some studies, more than half of people experience heart failure.
A study conducted in 2023 concluded that sleeping on the right side can help patients with heart conditions. In this position, sleepers may experience less pressure on their hearts. The study’s outcomes also indicated that right-side sleeping helps stabilize blood pressure and heart rate.
While side sleeping offers various benefits, it may come with some disadvantages for certain individuals. Common disadvantages of side sleeping include:
1. Align Your Lower Body: Place a small pillow between your knees and ankles to maintain a horizontal alignment, preventing strain on hip and lower back muscles. Avoid crossing your legs, as this can lead to hip joint torsion and discomfort. Optimal alignment ensures a restful sleep.
2. Support Your Upper Body: Prevent upper-back twisting and muscle tension by placing a pillow between your arms and chest when sleeping on your side. This promotes a natural spine position, reducing stress on the chest and muscles for a more comfortable night’s sleep.
3. Choose the Right Pillow Height: Select a pillow of appropriate height to alleviate unnecessary neck pressure. Whether you prefer sleeping on your right or left side, maintaining a neutral spine position is essential. While sleeping on the left side may have minimal effects on ordinary individuals, those with cardiac insufficiency should prioritize safety and avoid left side sleeping due to potential risks associated with acute heart issues.
The fetal position is one of the most prevalent sleeping postures, characterized by curling up on your side with your knees drawn towards your chest. This cozy position often resembles the posture of a fetus in the womb, hence its name. Many individuals find comfort in this position, as it may help alleviate back pain and reduce snoring.
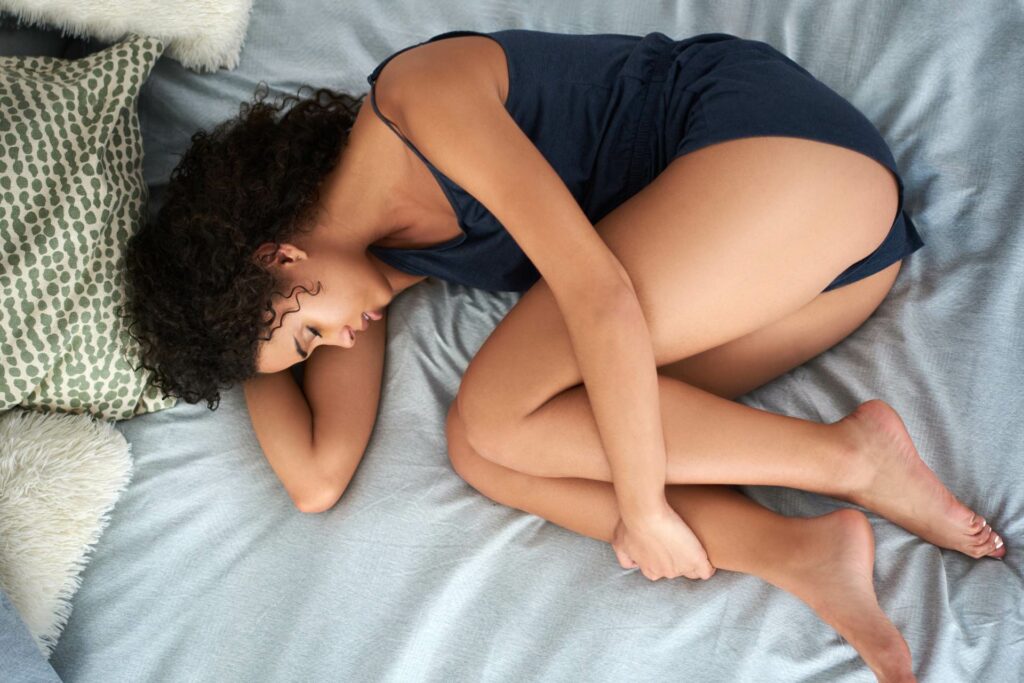

Curling up on your side promotes a natural alignment of the spine, potentially reducing the risk of back pain.
The fetal position may contribute to decreased snoring by keeping the airways open and unobstructed.
Sleeping in the fetal position can increase your sense of security and comfort like no other.
The freefall position, commonly known as stomach sleeping, is a sleep posture where individuals lie face down with their arms positioned near or under the pillow. While this position may offer a sense of comfort for some, it comes with both benefits and considerations.

The freefall position, or stomach sleeping, does offer certain benefits to those who find this posture comfortable.
Choosing to lie on your stomach offers a potential solution for those looking to reduce snoring during sleep. This freefall sleep position promotes a more open airway, effectively minimizing the vibrations in the throat that often contribute to snoring sounds.
When you sleep on your stomach, gravity assists in keeping the air passages clear, preventing the soft tissues in the throat from collapsing and causing the distinctive sound of snoring.
Individuals with mild sleep apnea may find relief in the belly position. This sleep posture can facilitate improved breathing by helping to keep the airways open during sleep. Mild sleep apnea is characterized by occasional disruptions in breathing patterns, and the face-down position may minimize the likelihood of these interruptions. Stomach sleeping encourages a more natural alignment of the air passages, potentially reducing the occurrence of breathing obstructions.
Some individuals find the face-down position comforting, contributing to a sense of security and promoting relaxation during sleep. This can be attributed to the psychological and emotional aspects of the sleep posture. Sleeping in this position may mimic a fetal-like position, which is instinctively associated with safety and comfort.
Individuals who find the face-down position comforting might include those experiencing feelings of loneliness or dealing with depression. The act of curling up or lying face down can create a cocoon-like feeling, providing a perceived sense of protection and emotional security.
Sleeping on your stomach may put a strain on your neck and spine, increasing the risk of pain and discomfort. While it may be a preferred position for some individuals, there are important risks and considerations to keep in mind. The table below outlines these risks and considerations associated with stomach sleeping:
| Risks | Considerations |
| Strain on neck and spine | May worsen pre-existing back, neck and sciatic pain |
| Restricted chest movement | Can make breathing harder and require more energy |
| Increased risk of sleep apnea | May lead to poor sleep quality and daytime fatigue |
| Potential for facial wrinkles | Pillow contact can cause skin irritation and wrinkles |
Considering these risks, it may be best to avoid stomach sleeping if you experience back or neck pain. However, if it’s a comfy position for you, using a supportive pillow and mattress can help alleviate some of the strain on your body. It’s always important to prioritize your comfort and well-being when choosing a new position for a restful sleep.
Finding the best position to sleep can greatly improve your sleep quality and overall well-being. Certain sleeping positions can help with your issues, while other common sleep positions can make them even worse.
To summarize, we’re inviting you to take a brief look at the table below, which categorizes all the sleeping positions along with their corresponding health benefits and risks:
| Sleep Position | Benefits | Risks |
|---|---|---|
| Sleeping on your back | Reduced acid reflux, decreased risk of wrinkles, reduces lower back pain | Worsened snoring, sleep apnea |
| Sleeping on you left side | Improved back alignment, aids digestion and reduces snoring, best for pregnant women, alleviates back and neck pain | Numbness or tingling in arms and hands, shoulder pain, pressure on internal organs, formation of facial wrinkles |
| Sleeping on your right side | Reduced pressure on the heart, stabilized blood pressure and heart rate | Increased risk of wrinkles, potential worsening of acid reflux |
| Sleeping in a fetal position | Promotes natural alignment of the spine, reduces snoring, provides a sense of security | Potential for joint discomfort, restricted breathing |
| Sleeping on your stomach | May reduce snoring, potentially relieve sleep apnea, provide a sense of security and relaxation | Increased risk of neck and back pain, restricted chest movement, worsened sciatica |
As you can see, sleeping position matters and can improve the quality of your sleep. Adjusting to a new sleep position may take some time but it’s worth the hassle as it can help when you have problems sleeping.
Before you start, measure your sleep quality to see if a wrong sleep position potentially impacts your sleep. For this, consider trying the ShutEye® app for free!
Anna Linens. (2012). National Sleep Survey Pulls Back The Covers On How We Doze And Dream. [Online] Available at: https://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/national-sleep-survey-pulls-back-the-covers-on-how-we-doze-and-dream-184798691.html
Leung, R. S. T., Bowman, M. E., Parker, J. D., Newton, G. E., & Bradley, T. D. (2003). Avoidance of the left lateral decubitus position during sleep in patients with heart failure: Relationship to cardiac size and function. [Online] Available at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12535814/
Cary, D., Briffa, K., & McKenna, L. (2019). Identifying relationships between sleep posture and non-specific spinal symptoms in adults: A scoping review. BMJ Open, 9(6), e027633. [Online] Available at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31256029/
Dainese, R., Serra, J., Azpiroz, F., & Malagelada, J. R. (2003). Influence of body posture on intestinal transit of gas. Gut, 52(7), 971–974. [Online] Available at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12801953/
Giuffre BA, Jeanmonod R. (2022). Anatomy, Sciatic Nerve. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Accessed 5/21/2023. [Online] Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482431
Ravesloot, M. J., van Maanen, J. P., Dun, L., & de Vries, N. (2013). The undervalued potential of positional therapy in position-dependent snoring and obstructive sleep apnea: A review of the literature. Sleep & breathing, 17(1), 39–49. [Online] Available at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22441662/
Leung, R. S. T., Bowman, M. E., Parker, J. D., Newton, G. E., & Bradley, T. D. (2003). Avoidance of the left lateral decubitus position during sleep in patients with heart failure: Relationship to cardiac size and function. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 41(2), 227–230. [Online] Available at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12535814/
Naughton, M. T., & Lorenzi-Filho, G. (2009). Sleep in heart failure. Progress in Cardiovascular Diseases, 51(4), 339–349. [Online] Available at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19110135/
Anson, G., Kane, M. A. C., & Lambros, V. (2016). Sleep wrinkles: Facial aging and facial distortion during sleep. Aesthetic Surgery Journal, 36(8), 931–940. [Online] Available at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27329660/
Pain in the Back, Neck, and Extremities. In: Ropper AH, Samuels MA, Klein JP, Prasad S, eds. Adams and Victor’s Principles of Neurology. 12th ed. McGraw Hill; 2023.
Neill; et al. (January 1997). “Effects of sleep posture on upper airway stability in patients with obstructive sleep apnea”. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, 155(1), 199–204. [Online] Available at: https://www.atsjournals.org/cgi/content/abstract/155/1/199
Fujiwara Y, Arakawa T, Fass R. (2013). Gastroesophageal reflux disease and sleep. Gastroenterol Clin North Am, 42(1), 57-70.