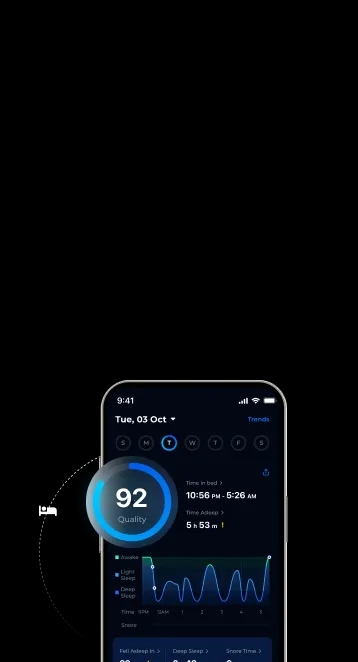


Are you someone who prefers to curl up in the fetal position when you sleep? Wonder if this position is beneficial or has any drawbacks? In this article, we’ll explore side sleeping in the fetal position and whether it’s the ideal position for a good night’s rest.
Sleeping on your side, particularly in the fetal position, can have several advantages.
If you’re pregnant or have obstructive sleep apnea, sleeping in the fetal position may be beneficial for you.
The fetal position is when you sleep on your side and bring your knees up to your chest, mimicking the position of a fetus in the womb.
Pregnant individuals, especially in the later stages of pregnancy, may find the fetal position beneficial. Sleeping on your left side, in particular, can reduce pressure on your heart during pregnancy.
People with obstructive sleep apnea may also benefit from sleeping in the fetal position. This sleep position can help keep the airway open and reduce episodes of interrupted breathing during sleep.

Sleep positions can significantly impact the quality of your sleep. One sleep position that affects sleep quality is the fetal position. This is when you sleep on your side and bring your knees up to your chest, mimicking the position of a fetus in the womb.
Sleeping in the fetal position may have several benefits. It’s a preferred sleeping position for pregnant women as it improves circulation to the baby. Additionally, sleeping on your left side in the fetal position can reduce pressure on your heart during pregnancy.
On the other hand, sleeping on your stomach isn’t recommended as it can lead to low back and neck pain and may cause you to toss and turn more frequently.
Nightmares and daytime sleepiness can have various causes that can affect the quality of your sleep. It is important to understand the root causes of these issues in order to find effective solutions. Here are some common causes and solutions for nightmares and daytime sleepiness:
| Causes | Solutions |
|---|---|
| Stress and anxiety | Practice relaxation techniques such as deep breathing or meditation before bedtime. Seek therapy or counseling to manage stress. |
| Medications | Consult with your healthcare provider to see if alternative medications can be prescribed. |
| Sleep disorders | Seek medical evaluation and treatment for sleep disorders such as sleep apnea or narcolepsy. |
| Traumatic experiences | Consider therapy or counseling to address and process the trauma. Engage in stress-reducing activities during the day. |
| Insufficient sleep at night | Prioritize and schedule enough time for sleep. Create a consistent sleep routine. |
| Poor sleep quality | Evaluate and improve sleep hygiene practices. Create a comfortable sleep environment. |
| Medical conditions | Consult with a healthcare provider to address underlying medical conditions that may contribute to daytime sleepiness. |
| Lifestyle factors | Limit alcohol consumption and avoid excessive caffeine intake. Maintain a healthy diet and exercise regularly. |
To prioritize your health and well-being, it’s crucial to recognize the significance of getting sufficient sleep. Sleep plays a vital role in maintaining overall health and well-being.
Adequate sleep is essential for cognitive function, memory consolidation, and emotional balance. It also plays a role in preventing chronic conditions like obesity and diabetes. Quality sleep supports immune system function and helps prevent illness.
Moreover, sleep deprivation can impair judgment, increase the risk of accidents, and negatively impact mental health. By practicing good sleep habits and prioritizing rest, you can enhance your physical and mental well-being.

To optimize your sleep quality and promote overall well-being, it’s important to consider the impact of your diet on your sleep. Your dietary choices can greatly influence the quality and duration of your sleep.
Here are three ways your diet can impact your sleep:
1. Certain foods can promote better sleep: Foods like cherries and bananas are rich in melatonin, a hormone that regulates sleep-wake cycles. Incorporating these foods into your diet can help improve your sleep quality.
2. Avoiding heavy meals close to bedtime: Eating heavy meals close to bedtime can lead to discomfort and indigestion, making it difficult to fall asleep. It’s recommended to have your last meal at least 2-3 hours before bedtime to prevent sleep disturbances.
3. Be mindful of caffeine and alcohol consumption: Consuming caffeine and alcohol close to bedtime can interfere with your sleep. Caffeine is a stimulant that can keep you awake, while alcohol can disrupt your sleep cycle and lead to fragmented sleep.
In conclusion, side sleeping in the fetal position can be a beneficial sleep position for certain individuals. It can provide comfort for pregnant women, alleviate back pain, and potentially improve symptoms of obstructive sleep apnea.
However, it may not be ideal for everyone, as individual preferences and physical conditions vary. It’s important to find the sleep position that works best for you and promotes a good night’s rest.
Remember to prioritize sleep for overall health and well-being, and consider other factors such as diet and sleep environment for optimal sleep quality.
American Pregnancy Association (n.d.) Best Sleeping Positions While Pregnant [online]. Available at: https://americanpregnancy.org/healthy-pregnancy/pregnancy-health-wellness/sleeping-positions-while-pregnant/
University of Rochester Medical Center (n.d.) Sleeping Positions During Pregnancy [online]. Available at: https://www.urmc.rochester.edu/encyclopedia/content.aspx?contenttypeid=85&contentid=p01238