

Sleeping in every once in a while is not a bad thing. However, consistently oversleeping— especially if your sleep duration regularly exceeds the recommended amount, can sometimes lead to negative health problems.
Let’s find out the causes of oversleeping, side effects, and ways to stop sleeping excessively.
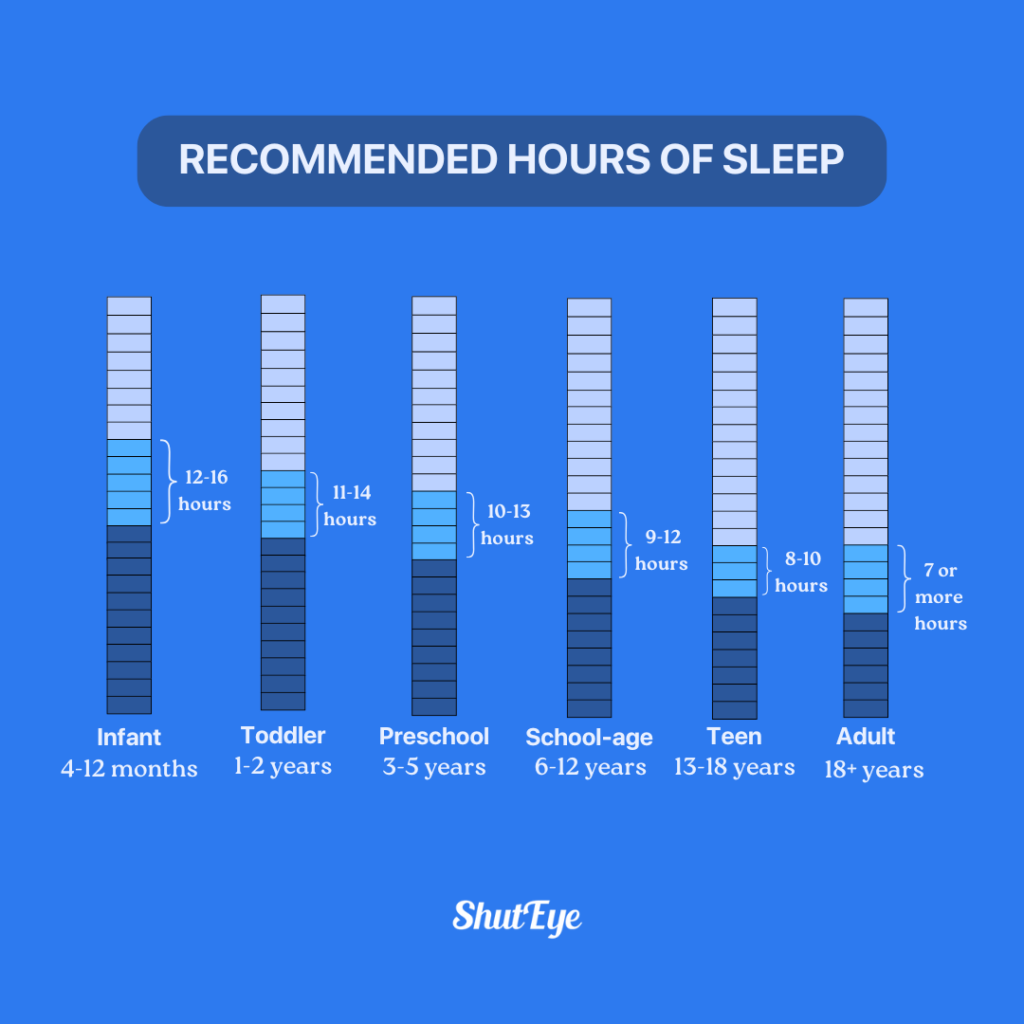
According to experts, adults on average need between seven and nine hours of sleep each night to function properly [1]. For children, the recommended amount of sleep is between eight to sixteen hours depending on age.


Getting nine or more hours of sleep is not necessarily bad for you if it happens occasionally. Sometimes, a person may sleep more if they are recovering from sleep deprivation or if they are feeling ill.
It only becomes a problem if you always oversleep to feel well-rested at night.

Consistently oversleeping is likely to be the result of an underlying medical condition or a sleep disorder. Some of the common causes are [2]:
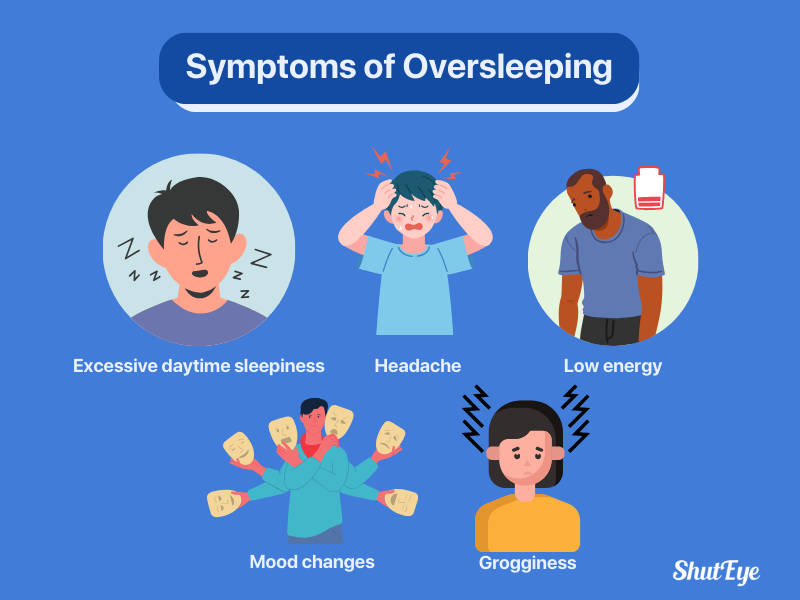
Some people may need a longer sleep, so sleeping more than the recommended amount is not always a cause for concern.
However, if you are sleeping more than you need to, you may experience symptoms like [3]:

The answer is yes, oversleeping can make you feel tired. Getting too little or too much sleep can disrupt your sleep-wake cycle and significantly alter your perception of fatigue [4]. This means that if you were to sleep in on the weekend or snooze for too long, you may find yourself feeling sleepier than usual.
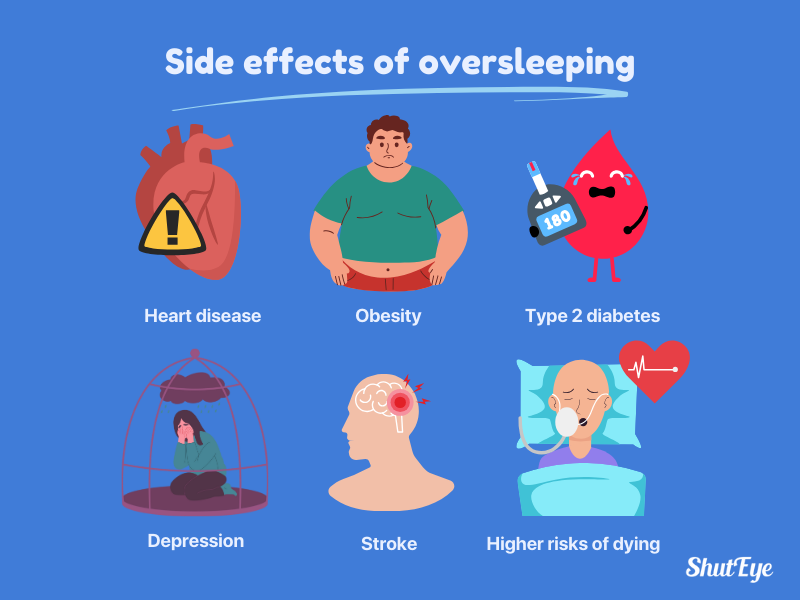
Excessive sleep may have detrimental effects on your physical and mental well-being. Sleeping too much can put you at risk of the following health issues:
These effects can be attributed to disrupted sleep patterns and an imbalance in sleep needs. While occasional oversleeping to catch up on sleep debt or illness is considered normal, chronic oversleeping may indicate an underlying sleep disorder.
If you frequently experience excessive sleep and its associated effects, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for a thorough sleep study and evaluation.
You can prevent yourself from sleeping too much by improving your sleep habits. Here are four tips to avoid excessive sleep:
1. Maintain a regular sleep schedule: Try to go to bed and wake up at the same time every day, even on weekends. This helps regulate your body’s circadian rhythm and promotes better sleep each night.
2. Create a sleep-friendly environment: Make sure that your sleep environment is dark, quiet, and cool. Use curtains or blinds to block out light, wear earplugs or use a white noise machine to drown out noise, and set your thermostat to a comfortable temperature.
3. Limit exposure to blue light before bed: Avoid using electronic devices such as smartphones and tablets before bedtime, as the blue light emitted by these devices can delay sleep onset. Instead, engage in relaxing activities like reading a book or taking a warm bath.
4. Be mindful of your lifestyle habits: Avoid consuming caffeine or exercising close to bedtime, as these can stimulate your body and make it harder to fall asleep. Also, try to maintain a healthy diet and manage stress levels, as these factors can impact your sleep quality.
In conclusion, oversleeping can have various causes and affect your health and well-being. Factors such as poor sleep hygiene, underlying health conditions, or sleep disorders can contribute to oversleeping.
To improve your sleep patterns and avoid excessive sleepiness, consider using the ShutEye® app. ShutEye® is a science-backed sleep app that tracks your sleep cycle, offering personalized insights to help you achieve quality sleep.
Cleveland Clinic (2023) Oversleeping: What Is It, Why Is It Happening and How Do I Make It Stop? [online]. Available at: https://health.clevelandclinic.org/oversleeping
Harvard Health Publishing (2019) Are you tired from...too much sleep? [online]. Available at: https://www.health.harvard.edu/staying-healthy/are-you-tired-from-too-much-sleep
Lawler, M. (2024) Are You Sleeping Too Much? Signs, Outlook, and Complications [online]. Available at: https://www.everydayhealth.com/sleep/are-you-sleeping-too-much/#signs
National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute (2022) How Much Sleep Is Enough? [online]. Available at: https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/sleep/how-much-sleep