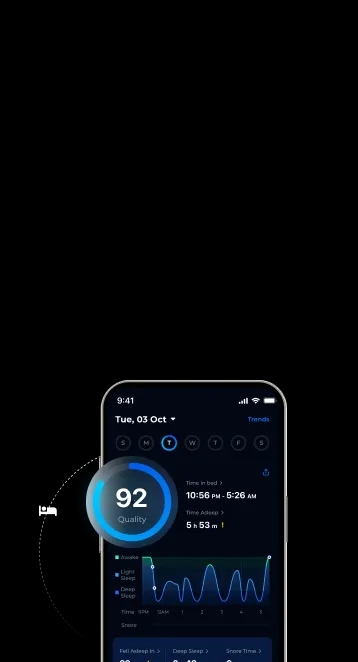


When you are overly stressed from work or personal responsibilities, you may experience insomnia. Cortisol, the stress hormone, plays a crucial role in regulating our sleep-wake cycle among others. In this article, we will explore the relationship between cortisol and sleep.
Understanding how cortisol affects our sleep can help you find ways to achieve a more restful night’s rest.
Cortisol is a steroid hormone that is made in the cortex of the adrenal glands. It is produced by the hypothalamic pituitary adrenal axis (HPA axis) and is responsible for many functions within the body, including the body’s stress response, regulating metabolism, inflammatory response, and immune function [1].
Cortisol also plays a role in regulating blood pressure and controlling the sleep-wake cycle, also known as circadian rhythm [2].
According to research, it’s likely that cortisol is linked to more restless and fragmented sleep. When we lack sleep or experience sleep loss, it triggers our body’s stress response which results in higher cortisol production. Higher stress levels make it harder to fall asleep and increase sleep disruption [3].
In a study that was done in 2014, it was found that sleep deprivation can increase cortisol levels, creating a vicious cycle of poor sleep and heightened stress [4]. It’s essential to prioritize sleep and manage stress levels to maintain a healthy cortisol balance and improve your sleep quality.
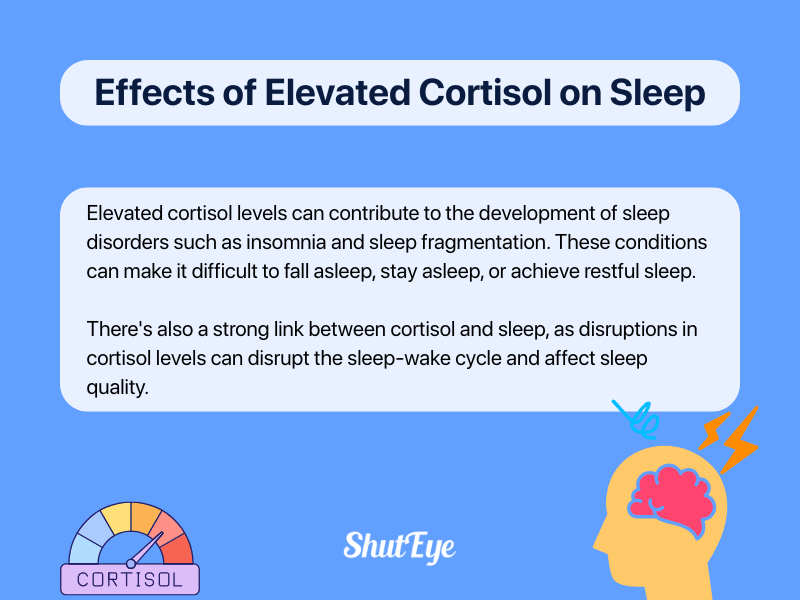
When the stress hormone, cortisol is elevated in the evening, it can disrupt your sleep, leading to various effects on your sleep quality and overall well-being. Here are two key effects of elevated cortisol on sleep:
Understanding the effects of elevated cortisol on sleep can help you take steps toward improving your sleep quality and overall well-being.
Having normal cortisol levels is important as it plays a role in how the body is regulated to function properly. There are two types of cortisol imbalance — hypercortisolism and hypocortisolism [1].
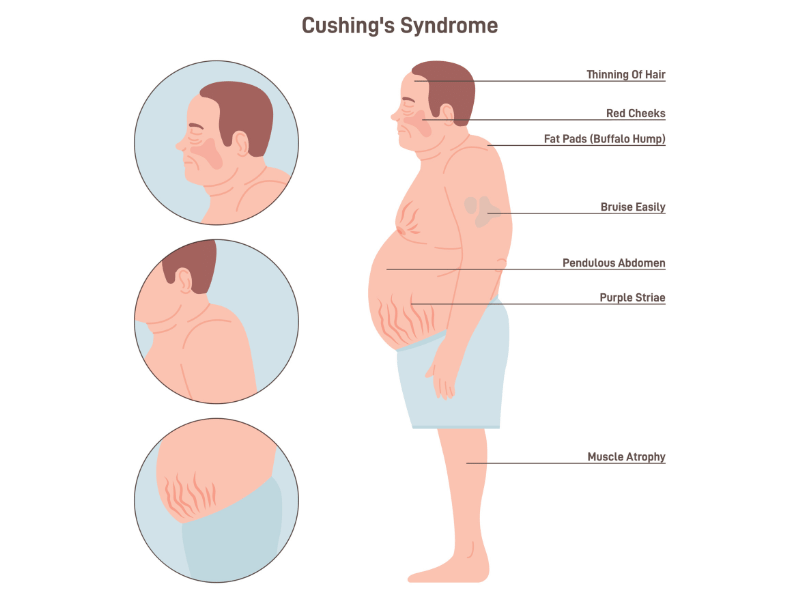
Hypercortisolism or high cortisol levels can be caused by various factors such as a tumor on the adrenal glands, or excessive oral or injectable corticosteroid use. When you have too much cortisol in your body, it may lead to Cushing syndrome.
Cushing syndrome is associated with symptoms such as:
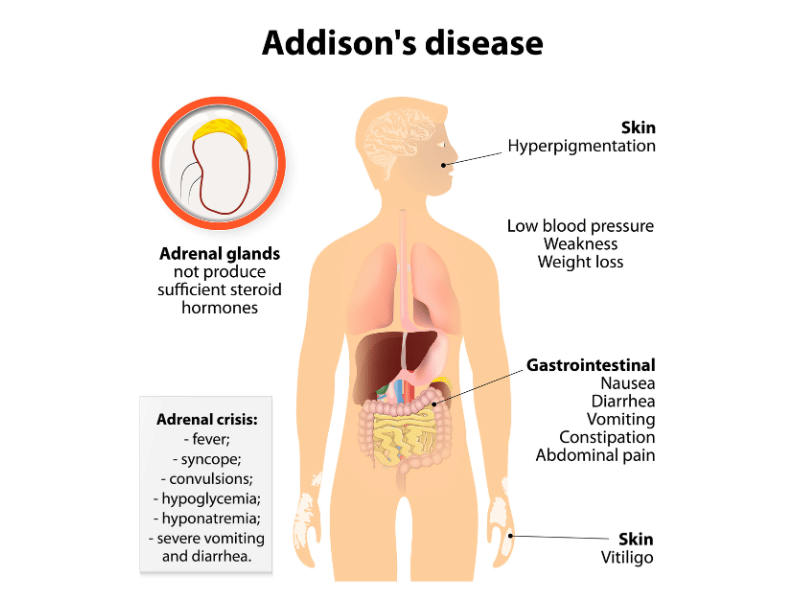
Hypocortisolism or low cortisol levels can lead to two types of conditions which are primary adrenal insufficiency and secondary adrenal insufficiency.
Primary adrenal insufficiency, also known as Addison disease, happens when your body starts to attack your adrenal glands or the adrenal cortex. Some other causes may also include infection or a malignant tumor on the adrenal glands.
Secondary adrenal insufficiency, which is an insufficient production of ACTH, can be caused by pituitary disease or more commonly, the use of corticosteroids.
Some symptoms of adrenal insufficiency include:
Cortisol regulation is important to prevent an imbalance in your body functions. In cases where cortisol dysregulation becomes severe, it may be necessary for you to seek medical intervention. Consulting a healthcare professional can help you identify some of the underlying causes and decide on the appropriate treatment moving forward.
To effectively manage cortisol levels, incorporating stress-reducing activities into your daily routine is key. Here are some tips to help you manage cortisol levels and improve your sleep:
If you want to reduce your stress level, you don’t want to be engaging in activities that increase it. Instead, you want to opt for non-stressful activities such as listening to calming music, reading a book, or even picking up a relaxing hobby.
Picking up a new hobby can be a rewarding experience as you give your brain something new to focus on. Relaxing hobbies include painting, gardening, cooking, or learning to play a new instrument.
You also want to ensure that you are prioritizing good sleep hygiene practices. Good sleep hygiene is what will help you to improve your sleep quality in the long term.
Some practices include establishing a consistent sleep schedule, creating a relaxing bedtime routine, and ensuring that your sleep environment is comfortable and conducive for sleep. Establishing a consistent sleep schedule, even on the weekends can help to signal to your brain when it’s time to sleep and when it’s time to wake up. This will make it easier for you to fall asleep faster and wake up easier.
Creating a relaxing bedtime routine by reading, taking a warm bath, or stretching can also help to signal to your body that it is time to wind down for bed. Additionally, you want to have a sleep environment that is dark, quiet, and cool for optimal rest.
Engaging in regular physical activity can also help to reduce the cortisol production in your body and improve sleep quality. However, you should be mindful to engage in activities that are not too intense and stressful on your body. Instead, opt for low-intensity exercises such as walking, cycling, swimming or stretching.
You may also try relaxation techniques to induce a relaxation response in the body. This will encourage your body to produce less cortisol.
Some examples include:
Additionally, you choose to avoid consuming caffeine if you are prone to symptoms of anxiety as it is a stimulant that speeds up brain activity. This could increase feelings of anxiety and stress in the body, making it hard for you to fall asleep.
You should also avoid consuming food or beverages that contain caffeine, especially when it is closer to the evening. This is because it can interfere with your ability to fall asleep at night.
Last but not least, you want to follow a balanced diet. It is suggested that consuming a diet that is rich in dietary fibers, omega-3 fatty acids, and aged, fermented, or cultured foods can help with reducing stress, and ensure a stable cortisol level [5].
Try to consume more vegetables, fruits, beans, nuts, fish, seafood, yogurt, and apple cider vinegar.
By understanding the connection between cortisol and sleep and taking steps to balance it, you can improve the quality of your sleep.
If you’re experiencing ongoing sleep disturbances, extreme fatigue, persistent symptoms of insomnia, or signs of high or low cortisol—such as unexplained weight changes, anxiety, or frequent awakenings—it may be a good time to see a doctor.
Chronic stress and cortisol imbalances can disrupt your sleep cycle, leading to long-term health issues if left unaddressed. Seeking help from a healthcare professional can help you assess your symptoms through blood tests and recommend proper interventions or stress management techniques.
In conclusion, cortisol, the stress hormone, plays a significant role in regulating our sleep-wake cycle and overall well-being. By managing cortisol levels through effective strategies like stress reduction techniques, exercise, and a healthy lifestyle, we can promote better sleep and improve our overall sleep quality.
Try the ShutEye® app to monitor your sleep, uncover insights, and discover relaxation techniques that support a healthier sleep routine. Take control of your rest—because better sleep starts with better awareness!
Dusang, K. (2019) How stress can affect your sleep [online]. Available at: https://www.bcm.edu/news/how-stress-can-affect-your-sleep
Minkel, J., Moreta, M., Muto, J., Htaik, O., Jones, C., Basner, M., & Dinges, D. (2014) Sleep deprivation potentiates HPA axis stress reactivity in healthy adults. Health Psychology, 33(11), 1430–1434 [online]. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1037/a0034219
Naidoo, U. (2020) Eat to Beat Stress. American Journal of Lifestyle Medicine, 15(1), 39 [online]. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1177/1559827620973936
Thau L, Gandhi J, Sharma S. (2023) Physiology, Cortisol. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing [online]. Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK538239/
Watson, S. (2023) What Is Cortisol? [online]. Available at: https://www.healthcentral.com/condition/cushings-syndrome/what-is-cortisol