

Having stomach ulcers doesn’t just bring discomfort during mealtimes but also at night when you’re lying in bed. The burning, gnawing pain can make getting quality sleep feel almost impossible. But don’t worry, there are ways to find relief. Here, you’ll discover some sleep tips on how to sleep better with a stomach ulcer.

Stomach ulcers, also known as gastric ulcers, are open sores that develop on the lining of the stomach. Stomach ulcer is one of the two types of peptic ulcers, with duodenal ulcer being the other. Duodenal ulcers occur in part of the small intestine.
Both stomach ulcers and duodenal ulcers have similar symptoms and treatment options [1], [2].
Suffering from a stomach ulcer, also known as peptic ulcer disease, can be quite painful and disruptive to your sleep. However, there are steps you can take to help reduce the pain and promote ulcer healing while you sleep.
To manage stomach ulcer pain at night, you can make adjustments to your sleeping position and create a comfortable sleep environment. Here are 4 main strategies to help relieve stomach ulcer pain:
Stomach ulcers occur when the layer that protects the stomach lining is broken down. It is commonly caused by Helicobacter pylori infection and the use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
While researchers are not entirely sure how a person may become infected with the Helicobacter pylori bacteria, it is said that the bacteria is easily transmitted from person to person through contact with infected stool, vomit, or saliva. Consuming food or drinks that are already contaminated may also increase the risk of transmission [4].
Taking NSAIDs like aspirin, ibuprofen, and naproxen can also cause stomach ulcers as it thins the stomach lining, making it more prone to damage.
Some other possible causes include:

Avoiding certain foods is essential when managing a stomach ulcer, as they can cause painful flare-ups. To help you understand which foods to avoid, here are three key culprits that can trigger discomfort and worsen your ulcer symptoms:
By steering clear of these foods, you can reduce the risk of painful flare-ups, allowing you to sleep more comfortably with your stomach ulcer.
One of the most common symptoms of stomach ulcer is the feeling of a dull, gnawing pain in your stomach. Some may also experience symptoms of indigestion, nausea, vomiting, heartburn, and acid reflux [5].
Quit smoking and limit your alcohol intake to reduce the pain and discomfort associated with a stomach ulcer. Smoking and alcohol can increase stomach acid production and worsen ulcer symptoms. By quitting smoking, you can promote healing and improve your overall health.
Limiting alcohol consumption can also help reduce irritation to the stomach lining. It’s important to follow your doctor’s treatment plan for your stomach ulcer, which may include medication and lifestyle changes.
To reduce stress and manage your stomach ulcer symptoms effectively, it’s important to find healthy coping mechanisms and seek support from a healthcare professional or mental health expert. Stress doesn’t cause ulcers, but it can make symptoms worse and aggravate ulcer pain. Engaging in healthy stress-relieving activities can help manage symptoms and promote healing.
Here are three strategies to reduce stress and improve your overall well-being:
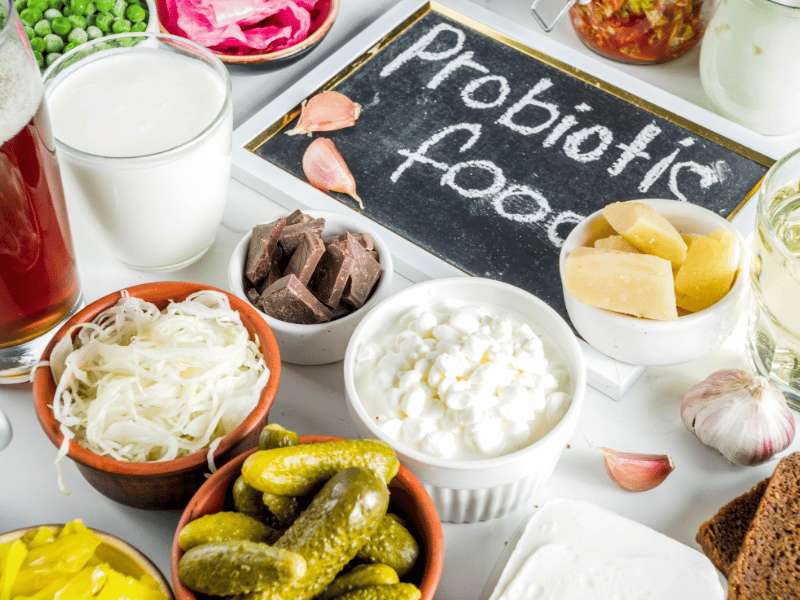

You can also consider taking probiotics as a natural home remedy to help balance the bacteria in your digestive tract. A healthy gut may help in killing off the H.pylori bacteria and reduce the side effects of antibiotics.
Some suggested foods for consumption are yogurt, kefir, kimchi, or probiotic supplements.
If your stomach ulcer was a result of H.pylori bacteria infection, your doctor may prescribe you antibiotics to kill off the bacteria and prevent stomach ulcers from forming again.
Alternatively, if the stomach ulcer was caused by using NSAID pain relievers, your doctor may treat you with proton pump inhibitors (PPI). It could take anywhere between a few weeks to a few months to recover, depending on the severity [6].
If you’re experiencing ongoing or severe symptoms of a stomach ulcer, it’s important to seek immediate medical attention.
Ongoing or severe symptoms may include persistent abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, blood in the stool, or unexplained weight loss. These symptoms could indicate a more serious condition or complications from the stomach ulcer.
Seeking medical attention is crucial because a healthcare professional can properly diagnose your condition and provide appropriate treatment options. They may recommend acid-reducing medications, antibiotics if there’s a bacterial infection, or other interventions to help alleviate your symptoms.
Getting a good night’s rest with a stomach ulcer may be difficult at first but by following strategies such as finding the right sleep position, avoiding trigger foods, and maintaining a relaxing bedtime routine — you can slowly ease discomfort and improve your sleep quality.
For more support to improve your sleep quality, consider trying the ShutEye® app. From personalized sleep tracking to relaxing soundscapes, ShutEye offers sleep tools that are designed to help you get better rest. Try it for free today!
HSE Live (2021) Stomach ulcer [online]. Available at: https://www2.hse.ie/conditions/stomach-ulcer/
National Insitute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (2023) Symptoms & Causes of Peptic Ulcers (Stomach or Duodenal Ulcers) [online]. Available at: https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/digestive-diseases/peptic-ulcers-stomach-ulcers/symptoms-causes
NHS (2022) Stomach ulcer [online]. Available at: https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/stomach-ulcer/
NHS Inform (2023) Stomach ulcer [online]. Available at: https://www.nhsinform.scot/illnesses-and-conditions/stomach-liver-and-gastrointestinal-tract/stomach-ulcer/
Penn Medicine (2023) Peptic Ulcer Disease [online]. Available at: https://www.pennmedicine.org/for-patients-and-visitors/patient-information/conditions-treated-a-to-z/peptic-ulcer-disease
Simadibrata, D. M., Lesmana, E., Amangku, B. R., Wardoyo, M. P., and Simadibrata, M. (2023) Left lateral decubitus sleeping position is associated with improved gastroesophageal reflux disease symptoms: A systematic review and meta-analysis. World journal of clinical cases, 11(30), 7329–7336 [online]. Available at: https://doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v11.i30.7329