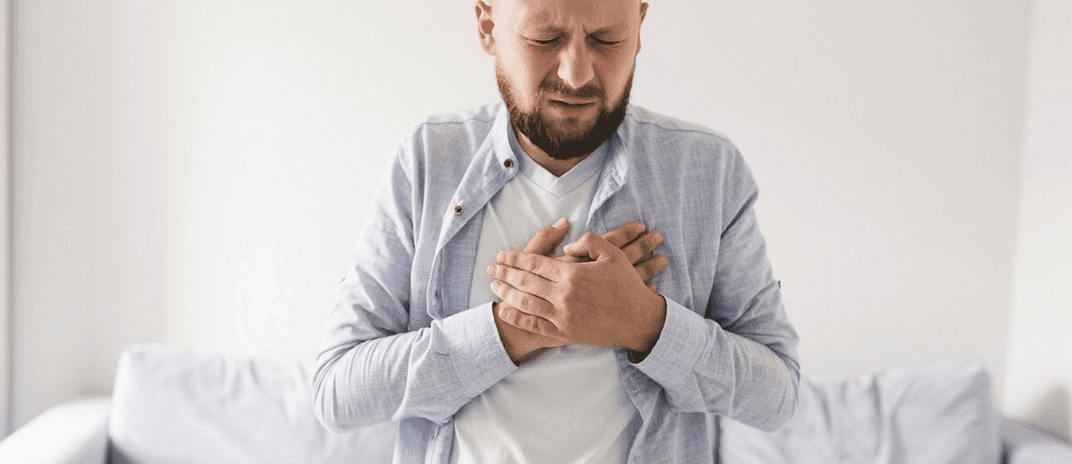


Do you struggle with acid reflux and find it hard to sleep well? You’re not alone.
Managing acid reflux is crucial for improving your sleep and overall well-being.
In this article, we’ll explore effective strategies and lifestyle changes to help you manage acid reflux and achieve a peaceful night’s rest.
We’ll discuss sleep positions that alleviate symptoms at night, lifestyle changes like avoiding trigger foods, and even medical interventions if needed.
By implementing these strategies, you can improve your sleep and effectively manage acid reflux symptoms.
To better manage your acid reflux and ensure a good night’s sleep, it’s important to understand how acid reflux occurs and its underlying causes.
Acid reflux, also known as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), happens when stomach acid escapes into the esophagus. The main symptom of acid reflux is heartburn, but it can also cause acid regurgitation, bloating, nausea, and belching. Acid reflux affects a significant portion of the global population, with up to 13% experiencing it at least once a week.
One way to improve sleep quality and manage GERD is by adjusting your sleep position. Sleeping on your left side can help reduce symptoms because gravity helps return stomach acid to the stomach. Avoid sleeping on your back or right side, as these positions can worsen acid reflux at night.
Understanding these factors and making small lifestyle changes can greatly improve your quality sleep and minimize nighttime acid reflux.
Choose the right sleep position to alleviate acid reflux discomfort and promote a restful night’s sleep. When experiencing acid reflux, it’s important to find the best sleep position that helps prevent stomach acid from flowing back into the esophagus. Here are four sleep positions that can provide relief:
Sleeping on your left side can provide several benefits for managing acid reflux and improving your sleep quality. It’s considered the best sleeping position for gastro-oesophageal reflux disease because it allows gravity to work in your favor. When you sleep on your left side, it helps prevent stomach acid from escaping into the esophagus. This position can be particularly helpful if you experience symptoms of GERD, such as heartburn, regurgitation, and bloating.
Sleeping on your left side also tends to reduce the severity and frequency of these symptoms compared to sleeping on your right side. So, if you want to get a good night’s sleep and manage your acid reflux, try sleeping on your left side and see if it makes a difference.
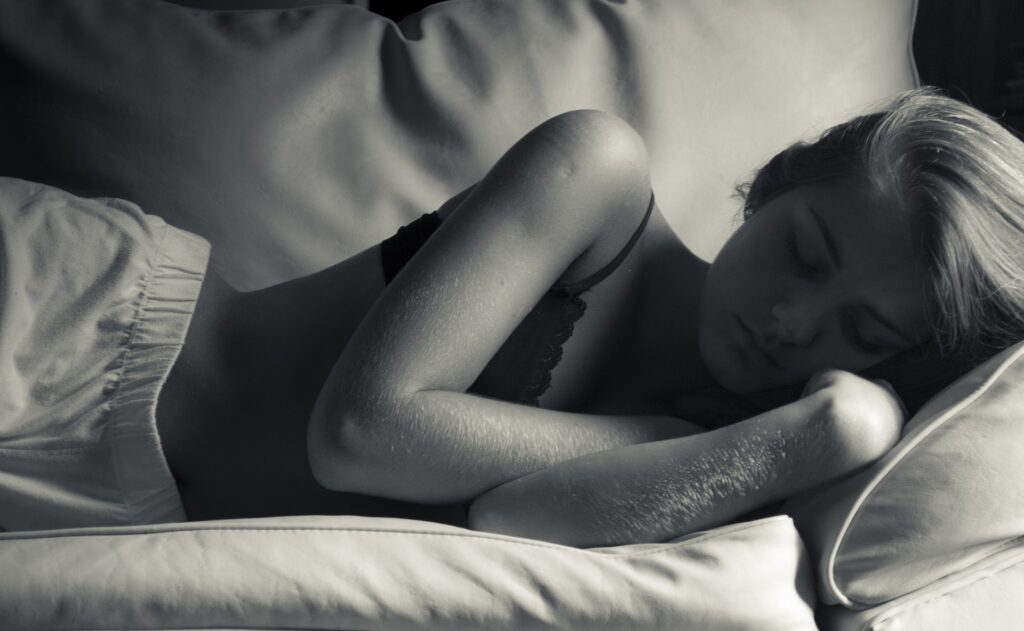

If you want to further improve your sleep quality and manage acid reflux, consider sleeping at an incline. Sleeping in this position can provide several benefits for reducing nighttime acid reflux and promoting heartburn relief.
Here are four reasons why sleeping at an incline makes acid reflux at night manageable:
To manage acid reflux effectively, make necessary lifestyle changes.
Lifestyle modifications can help alleviate severe symptoms of GERD and improve your sleep.
If lifestyle changes alone don’t alleviate your symptoms, consult a doctor for further evaluation and possible medical treatment options.
For effective management of acid reflux, consider medical interventions. When lifestyle changes and natural remedies don’t alleviate your acid reflux symptoms, medical interventions can provide relief. Here are four options to consider:
In conclusion, managing acid reflux is essential for achieving a good night’s sleep.
By understanding acid reflux and implementing lifestyle changes like sleeping on your left side or at an incline, avoiding trigger foods, and maintaining a healthy weight, you can effectively manage your symptoms.
If needed, medical interventions are available to provide further relief.
By prioritizing your acid reflux management, you can improve your sleep quality and overall well-being.
Mayo Clinic (2024) Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) [online]. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/gerd/symptoms-causes/