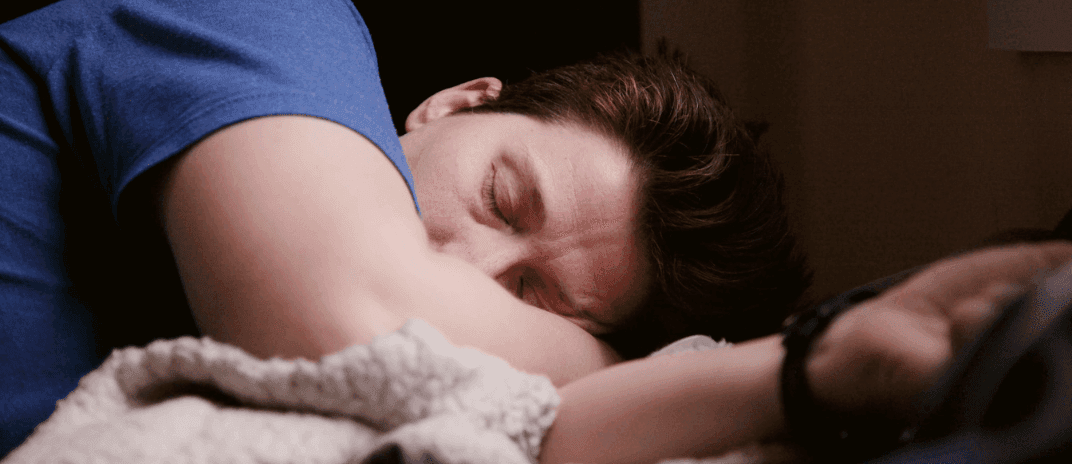
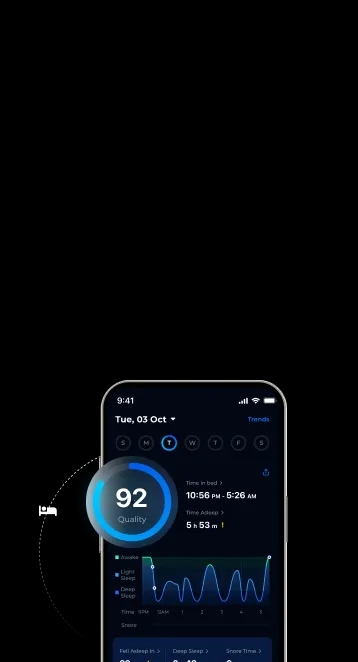


Deep sleep, one of the vital stages of the sleep cycle, is crucial for supporting both physical and mental well-being. It helps to support memory consolidation, learning, and repairing essential tissues in the body. So, how can you increase it to maximize the full benefits?
In this article, we’ll explore the importance of deep sleep and provide evidence-based strategies to improve your sleep quality.

When we go to sleep at night, our bodies will cycle through 4 different sleep stages— Non-Rapid Eye Movement (NREM) and Rapid Eye Movement (REM) sleep stages in the sleep cycle. Deep sleep, often referred to as slow-wave sleep, is a pivotal stage within the non-REM sleep cycle.
Deep sleep occurs during the first half of the night and is characterized by the presence of slow delta waves in brain activity. This stage is indispensable for both physical and mental rejuvenation, strengthening the immune system, and promoting optimal brain function and memory consolidation
Adults typically need different amounts of deep sleep, but the lack of it is associated with numerous health issues, including a higher risk of heart disease and Alzheimer’s disease [1].
During deep sleep, the brain waves slow down significantly, allowing for the consolidation of new information and the repair of the body and brain.
Research suggests that adults should aim for at least 90 minutes of deep sleep per night, although this can vary [2]. Those who don’t get enough of it may experience disruptions in physical and mental health, as well as impaired cognitive function.
| Age Group | Recommended Percentage of Total Sleep Time in Deep Sleep | Approximate Hours of Deep Sleep |
| Newborns (0-3 months) | 45-50% | 2.4-3.6 hours |
| Infants (4-11 months) | 25-30% | 2.8-3 hours |
| Toddlers (1-2 years) | 20-25% | 2.4-2.8 hours |
| Preschoolers (3-5 years) | 20-25% | 2.2-2.6 hours |
| School-age Children | 20-25% | 2-2.2 hours |
| Teenagers (14-17 years) | 10-20% | 1.7-2 hours |
| Adults (18-64 years) | 10-15% | 1.5-2.5 hours |
| Older Adults (65+ years) | 10-15%, may decrease compared to younger adults | Varies |
Related content:
How Much Deep Sleep Do You Really Need?
Age and Deep Sleep: How Much Do You Require?
As we know, the deep sleep stage plays a crucial role in ensuring that our brain gets proper rest and recovery. Getting enough of it can have great benefits on our health such as:
Deep sleep is important for releasing growth hormones and repairing tissues in your body. During this stage, your body releases growth hormone, which helps promote muscle, bone, and tissue repair. This repair process is crucial for overall health and recovery from injuries or intense physical activities.
Getting enough deep sleep can have significant benefits for your cognitive function and memory enhancement. It is a vital part of your sleep-wake cycle. It helps with memory consolidation as well as memory formation for emotional and non-emotional tasks [3]. You may experience cognitive function, memory, and even language learning difficulties without enough deep sleep.
So, prioritizing deep sleep can positively impact your overall brain health and performance.
Another benefit of getting a good amount of deep sleep is that it helps to strengthen your immune system and prevents you from falling sick so easily. When we fall asleep at night, our bodies produce a protein called cytokine. This protein helps our body to fight infection and inflammation as a normal immune response [4].
Allowing your body to rest can help to build resilience and adapt to these challenging times.
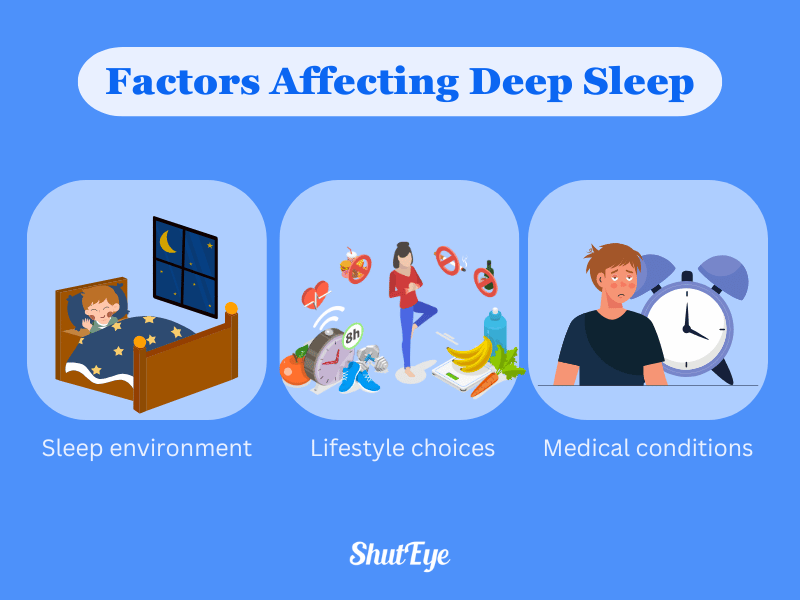
Factors that can impact the duration and quality of deep sleep are your sleep environment, lifestyle choices, and certain medical conditions. However, some factors can disrupt your deep sleep patterns.
Addressing these factors is crucial for ensuring a good night’s rest and maximizing the benefits of deep sleep for your health and well-being.

Sleep disorders can disrupt deep sleep and cause various disturbances. These disorders include sleep apnea, insomnia, restless leg syndrome, sleepwalking, and night terrors. Certain medications and substances can also affect deep sleep.
Here are some ways these sleep disorders can impact your restful state:
If you suspect you have a sleep disorder, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment options. They can help identify your specific sleep disorder and provide appropriate recommendations to improve your sleep quality.
Insufficient deep sleep can significantly impact your overall health and well-being. Deep sleep is important for memory consolidation, so not getting enough of it can affect your ability to remember and recall information. It can also weaken your immune system, making you more susceptible to infections. Moreover, disruptions in deep sleep have been linked to neurological conditions like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease.
In addition to these effects, sleep deprivation can lead to hormonal changes that can affect your appetite. This can potentially result in weight gain and increase your risk of developing insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes, and heart disease.
Many of us often wonder how to increase our deep sleep. We’ve created a video on “How to Get More Deep Sleep” in collaboration with Dr. June Seliber Klein, the Chief Medical Officer at Ognomy.
It’s important to note that both the duration and quality of deep sleep are crucial for overall health and well-being. In the next few sections, we’ll share tips on how to improve your deep sleep.
Ensuring you’re getting enough sleep each night is essential. Most adults require around 7-9 hours of quality sleep to function optimally. Establishing a consistent sleep schedule can significantly help. Try going to bed and waking up at the same time every day, including weekends. This regularity can regulate your body’s internal clock, making it easier to fall asleep and wake up feeling refreshed.

Creating a relaxing bedtime routine can signal your body that it’s time to wind down. Avoid engaging in stimulating activities or using electronics before bed, as these can disrupt your ability to fall asleep.
Instead, opt for calming activities such as reading a book, taking a warm bath, or practicing relaxation techniques like deep breathing or meditation. These practices can help calm your mind and prepare your body for a restful sleep.
Deep sleep is a crucial phase of our slumber that offers incredible benefits for our physical and mental well-being. It is pivotal in promoting growth, repairing the body, and enhancing cognitive function and memory retention. However, factors such as stress, insomnia, and aging can affect the quality and duration of deep sleep.
ShutEye® app offers an alternative solution for optimizing your sleep cycle and analyzing your sleep quality. You’ll receive personalized sleep recommendations based on your report to help you improve your overall sleep quality. Try it FREE for 7-days!
Institute of Medicine (US) Committee on Sleep Medicine and Research; Colten HR, Altevogt BM, editors. Sleep Disorders and Sleep Deprivation: An Unmet Public Health Problem. Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US); 2006. 3, Extent and Health Consequences of Chronic Sleep Loss and Sleep Disorders. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK19961/
Olson EJ. (2016). How many hours of sleep are enough for good health? https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/adult-health/expert-answers/how-many-hours-of-sleep-are-enough/faq-20057898
Saletin, J. M. (2020). Memory: Necessary for deep sleep? Current Biology, 30(5), R234–R236. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32155430/
Léger, D., Debellemaniere, E., Rabat, A., Bayon, V., Benchenane, K., & Chennaoui, M. (2018). Slow-wave sleep: From the cell to the clinic. Sleep Medicine Reviews, 41, 113–132. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29490885/
American Sleep Association.(n.d.). What is deep sleep? How to get more of it. https://www.sleepassociation.org/about-sleep/stages-of-sleep/deep-sleep/