

Struggling to fall asleep or manage stress levels? You may be missing a key ingredient in your diet. Magnesium is an essential mineral that is crucial in regulating sleep, supporting heart health, and calming the nervous system. In this guide, we’ll explore 10 magnesium-rich foods that not only help you catch better Zzzs but also keep your heart in top shape.
Magnesium is a mineral that is found in many foods, certain medications, and available as a dietary supplement. It is an essential mineral that helps more than 300 enzymes carry out the necessary bodily functions, including energy production, nerve function, and blood pressure and blood sugar regulation [1], [2].
Magnesium as a supplement can come in many forms with the most common being magnesium oxide, magnesium citrate and magnesium chloride
As mentioned, magnesium plays an important role in ensuring that over 300 biochemical reactions take place in our body, and it also acts as an electrical conductor so that our muscles can contract and our heart to beat steadily [1].
Besides the regulation of our bodily functions and energy production, it helps to reduce high blood pressure and lower the risk of heart disease as well as ensure good sleep health.
One of the ways that magnesium can help promote better sleep health, according to research, is that it helps to regulate gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) levels. GABA is a neurotransmitter that plays a role in calming the nervous system down. Additionally, it also helps to promote melatonin production and reduce cortisol levels, which can disrupt sleep [3].
The recommended dietary allowance of magnesium differs for both males and females. For adult males between the ages of 19 to 50+ years old, it is recommended to get up to 400-420 mg of magnesium daily, and 310-320 mg of magnesium daily for adult females.
For women who are pregnant, the recommended intake is 350-360 mg daily, and if you are lactating, 310-320 mg daily.
Here is a detailed table of the recommended dietary allowance of magnesium for reference [2]:
| Age | Male | Female | Pregnancy | Lactation |
| Birth – 6 months | 30 mg | 30 mg | ||
| 7 – 12 months | 75 mg | 75 mg | ||
| 1 – 3 years | 80 mg | 80 mg | ||
| 4 – 8 years | 130 mg | 130 mg | ||
| 9 -13 years | 240 mg | 240 mg | ||
| 14 – 18 years | 410 mg | 360 mg | 400 mg | 360 mg |
| 19 – 30 years | 400 mg | 310 mg | 350 mg | 310 mg |
| 31 – 50 years | 420 mg | 320 mg | 360 mg | 320 mg |
| 51+ years | 420 mg | 320 mg |
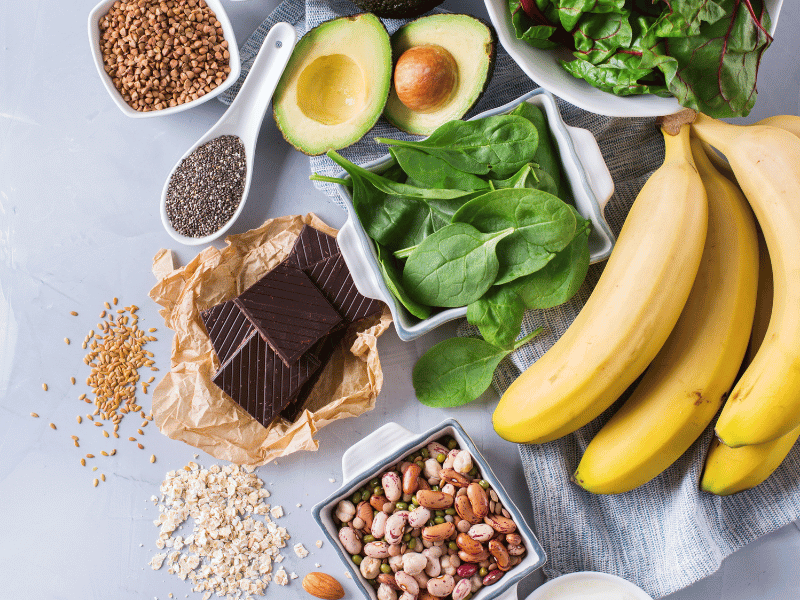

One of the best ways to ensure that you are meeting the daily magnesium requirement that you need is by taking magnesium supplements. That being said, not everyone may be comfortable with the idea of taking dietary supplements. But worry not, another way to ensure that you are getting adequate magnesium is by consuming magnesium-rich foods.
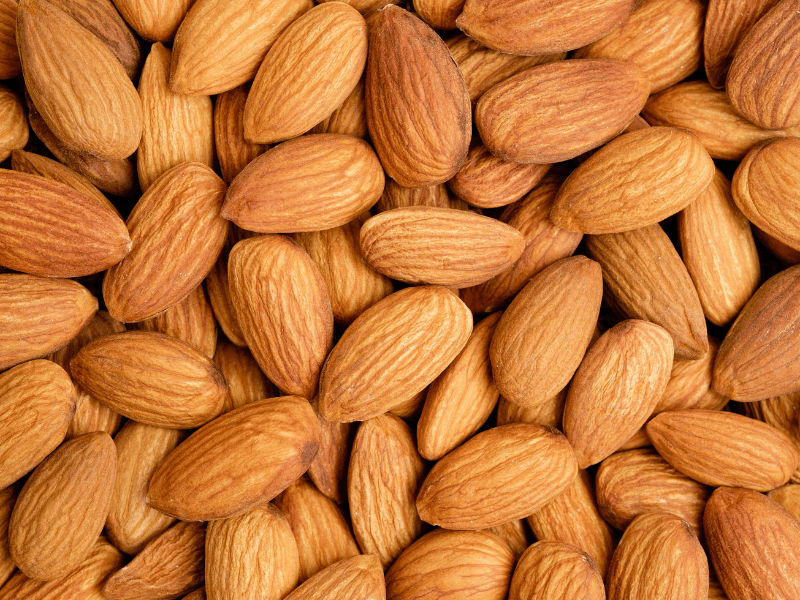

Almonds are a healthy snack that is also packed with a high amount of magnesium. For instance, 30g of almonds contains around 80 mg of magnesium. While it may not be enough to fulfill the daily intake that you need, snacking on them could still help to supplement your needs, especially if you are dealing with magnesium deficiency [4].
Avocados are known to be a good source of healthy fats and are also rich in essential vitamins to support a healthier heart and overall well-being. Each avocado has roughly 58 mg of magnesium content, which makes up a good portion of what we need in a day.
Avocados are also high in Vitamin B and Vitamin K, which are essential for energy production and bone health [4].
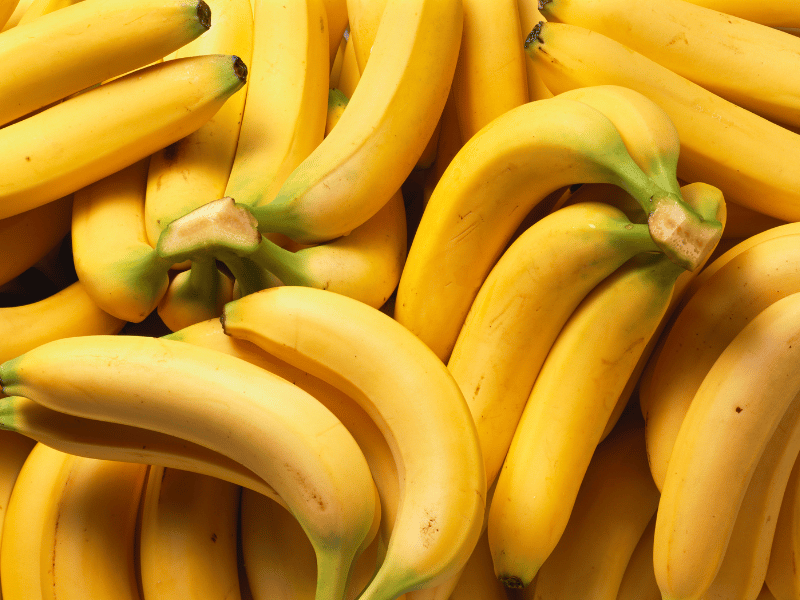

Banana is a fruit that is often praised for its high potassium content but did you know that they are also a good source of magnesium? A medium banana contains about 32 mg of magnesium, which makes it a great snack to consume to improve your dietary magnesium intake and support muscle and nerve function as well as your energy level [5].
Black beans are an excellent source of fiber and protein, offering around 15 g of protein and 15 g of fiber for 1 cup of cooked serving. Aside from this, they also pack quite a punch, offering 120 mg of magnesium per 1 cup of cooked black bean, supporting good heart health and digestion [6].
Don’t skip it the next time you order a salad or burrito bowl!
Great news for all you chocolate lovers out there— dark chocolate provides several benefits for your health. For one, dark chocolate is known for its anti-inflammatory, anti-diabetic and anti-microbial properties [7].
Consuming dark chocolate also helps to reduce the stress hormone, cortisol, so that you feel less stressed and more relaxed [8]. At the same time, it also contains an excellent amount of magnesium. According to the U.S. Department of Agriculture, a 100 g chocolate bar with 70-85% cacao solids contain 228 mg of magnesium. This is nearly half the daily magnesium requirement for an average adult [9].
Pumpkin seeds also makes a great snack to consume. They are rich in antioxidants, healthy fats and other minerals that help to enhance your bone mineral density and heart health. Additionally, pumpkin seeds are rich in the amino acid, tryptophan, which can be used to treat chronic insomnia. So for those who are struggling with insomnia and are looking to implement changes to their diet, this could be a good addition.
1 oz of serving of pumpkin seeds also contains a high amount of magnesium (156 mg) [10].
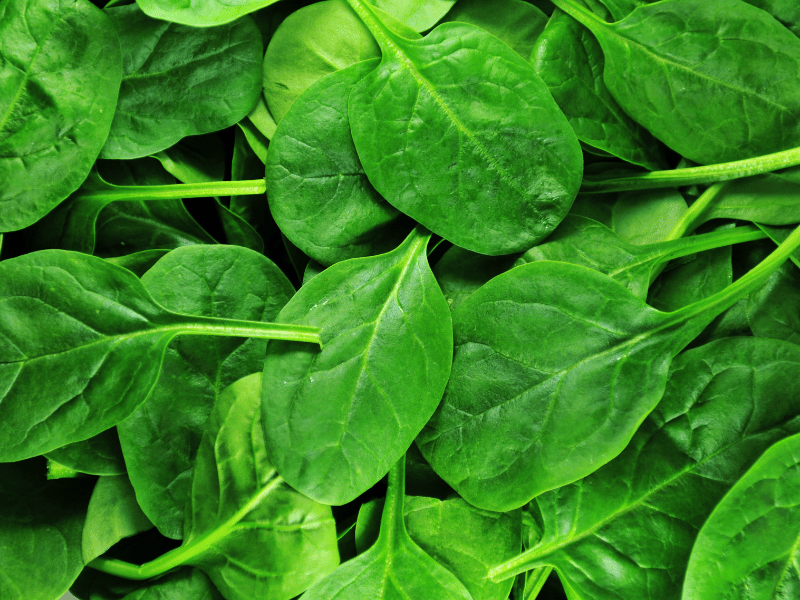

I’m sure that for many of us, the first thing that comes to mind when we think of spinach is Popeye the sailor. Popeye the sailor is a cartoon character who is famously known to consume a can of spinach to gain immense strength instantly.
Well, the truth is that this leafy green is loaded with a ton of nutrients. Consuming spinach is good for bone health, eyesight, immunity, supports good bowel health, and heart health [11].
It also contains a lot more minerals like magnesium, potassium, and iron compared to cabbage, lettuce, or broccoli.
Kale is also another vegetable that provides a good amount of nutrients. It is rich in fiber, antioxidants, calcium, iron, and essential vitamins like vitamin C and vitamin K [12].
While it may not offer as much magnesium as spinach does, it does offer a decent amount at 22.78 mg for 1 cup of raw kale [13]. So, kale is also a good option to add to your diet as a form of magnesium supplementation.
Tofu are also a great source of protein and nutrient-rich. It offers a solid plant-based source of magnesium—about 73 mg per 1 cup. It also provides protein and calcium, making it a fantastic option for vegetarians and vegans [14].
Whole grains like quinoa, brown rice, oats, and whole wheat bread are great magnesium sources. For example, 1 cup of raw quinoa contains about 357 mg of magnesium. Incorporating these into meals helps support overall heart and bone health [15].
Besides these 10 foods, there are also a variety of other food sources that are rich in magnesium, such as fatty fish ( e.g. salmon, mackerel, etc.), chickpeas, edamame, figs, cashews and lima beans. The list goes on!
Boosting your magnesium intake doesn’t have to be complicated — small, simple changes to your daily habits can make a big difference. Here are some easy tips to help you out:
Next time you’re at the store, reach for whole wheat bread, brown rice, oats, or quinoa instead of their refined versions. Whole grains are not just more nutritious — they also naturally carry more magnesium.
Instead of reaching for chips or candy, keep magnesium-friendly snacks like roasted pumpkin seeds, dark chocolate (yes, chocolate!), or trail mix handy. They’re delicious and good for you.
Be careful of drinking alcohol, caffeine, or eating processed foods, as it can lower your magnesium levels over time. Cutting back a little here and there can help you hang on to the magnesium you’re already getting.
If you find it hard to get enough magnesium through food alone, try taking magnesium supplements instead. Magnesium citrate and magnesium glycinate are usually easier on the stomach.
Before starting on any new supplements, you just want to make sure that you are checking with your doctor to ensure that it is safe for you to take. This is especially important if you are currently taking any other medications for an existing medical condition.
All in all, we need to get enough magnesium each day to ensure that we will have enough energy to get through the day, regulate our blood pressure and get better sleep. One of the ways to meet our daily magnesium needs is to consume foods that are rich in magnesium.
Alternatively, we can also achieve better sleep by using the ShutEye® app to track our sleep. By monitoring our sleep patterns, we can receive personalized insights that will help us to make informed decisions on improving it. Try it today for FREE!
Albakri, M. (n.d.) Spinach: Nutrition Facts and Health Benefits [online]. Available at: https://www.healthxchange.sg/food-nutrition/food-tips/spinach-nutrition-facts-and-health-benefits
Geng, C. (2023) Does magnesium help you sleep? [online]. Available at: https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/magnesium-for-sleep
Goldman, R. (2024) 10 foods high in magnesium [online]. Available at: https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/318595
John Hopkins Medicine (2025) The Benefits of Having a Healthy Relationship with Chocolate [online]. Available at: https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/wellness-and-prevention/the-benefits-of-having-a-healthy-relationship-with-chocolate
National Institute of Health (2022) Magnesium [online]. Available at: https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Magnesium-HealthProfessional/
Samanta, S., Sarkar, T., Chakraborty, R., Rebezov, M., Shariati, M. A., Thiruvengadam, M., and Rengasamy, K. R. (2022) Dark chocolate: An overview of its biological activity, processing, and fortification approaches. Current Research in Food Science, 5, 1916 [online]. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crfs.2022.10.017
The Nutrition Source (2023) Magnesium [online]. Available at: https://nutritionsource.hsph.harvard.edu/magnesium/
University of Rochester Medical Center (n.d.) Nutrition Facts- Bananas, raw, 1 medium [online]. Available at: https://www.urmc.rochester.edu/encyclopedia/content?contenttypeid=76&contentid=09040-5
University of Rochester Medical Center (n.d.) Nutrition Facts- Beans, black, mature seeds, cooked, boiled, without salt, 1 cup [online]. Available at: https://www.urmc.rochester.edu/encyclopedia/content?contenttypeid=76&contentid=16015-1
University of Rochester Medical Center (n.d.) Nutrition Facts- Kale, raw, 1 cup, chopped [online]. Available at: https://www.urmc.rochester.edu/encyclopedia/content?contenttypeid=76&contentid=11233-1
University of Rochester Medical Center (n.d.) Nutrition Facts- Tofu, raw, firm, prepared with calcium sulfate, 1 cup [online]. Available at: https://www.urmc.rochester.edu/encyclopedia/content?contenttypeid=76&contentid=16426-1
University of Rochester Medical Center (n.d.) Nutrition Facts- Quinoa, 1 cup [online]. Available at: https://www.urmc.rochester.edu/encyclopedia/content?contenttypeid=76&contentid=16426-1
USDA (2019) Chocolate, dark, 70-85% cacao solids [online]. Available at: https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/food-details/170273/nutrients
Ware, M. (2023) What are the health benefits of pumpkin seeds? [online]. Available at: https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/303864
Ware, M. (2024) What are the health benefits of kale? [online]. Available at: https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/270435