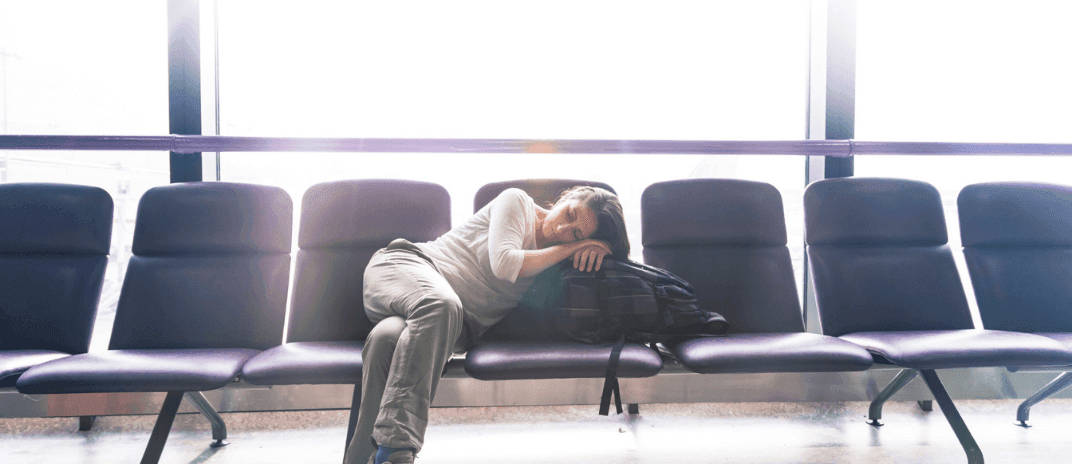


Have you ever experienced fatigue and an inability to sleep after a long-haul flight? You could be experiencing jet lag.
Jet lag, often dubbed the traveler’s curse, is a temporary disruption to our internal body clock, known as the circadian rhythm. In this article, we will explore what jet lag is, how it happens, and ways to prevent it the next time you decide to get on that flight.
Jet Lag is a temporary circadian rhythm sleep disorder, whereby there is inconsistency between the body’s internal clock and the external environment. Jet lag disorder generally happens as a result of traveling across multiple time zones [2].
The internal circadian clock helps to regulate various physiological and behavioral processes over a 24 hour-cycle. It can somewhat be seen as the body’s built-in timekeeper and controls circadian rhythms. Located in the brain’s hypothalamus, specifically the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN), it synchronizes with external cues like light and dark with the earth’s light-dark cycle [2].
The key functions of the internal circadian clock include:
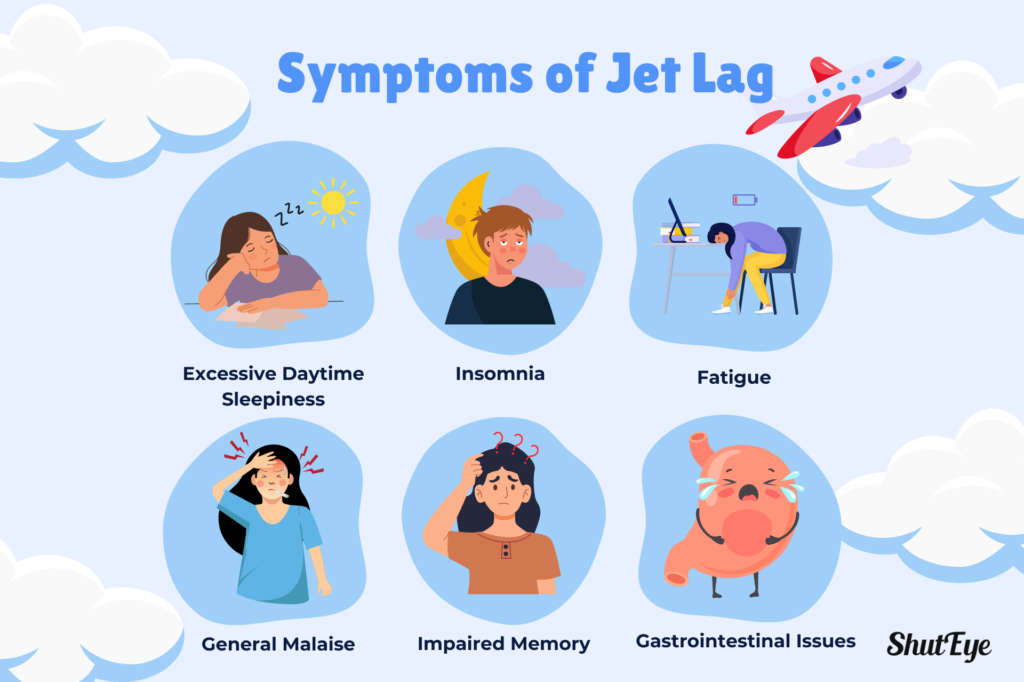
Jet lag can manifest through a variety of symptoms and usually occurs within a day or two. Some of the most common symptoms of jet lag include excessive daytime sleepiness, insomnia, fatigue, general malaise, impaired memory, and gastrointestinal issues.
In a survey conducted, it was found that 74% of surveyed travelers reported some form of jet lag. Additionally, 50% of these travelers reported symptoms of tiredness and fatigue. These findings underscore the impact of jet lag on individuals’ well-being and highlight the need for effective strategies to counter it.
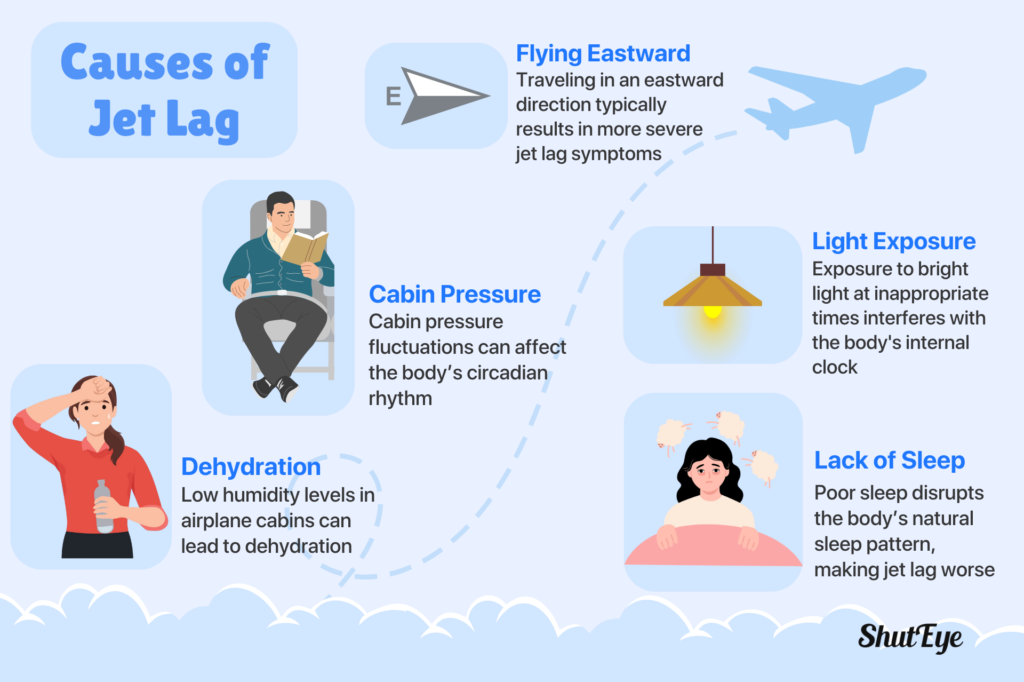
We have already established previously that jet lag is caused by traveling across time zones. However, that is not the only cause. Other contributing factors of jet lag include:
How long jet lag lasts would depend on various factors such as the number of time zones crossed, individual differences in circadian rhythm adjustment, and travel direction. Jet lag can last anywhere from a few days to a few weeks and would persist for 1-1.5 days per time zone crossed [3].
Ultimately, the actual duration of symptoms would depend on you as an individual and the trip you are taking.
Even though jet lag is not serious and is only temporary, it can lead to several complications that affect physical and mental well-being. This includes:
Experiencing prolonged or severe jet lag symptoms can contribute to the development of sleep disorders such as insomnia or hypersomnia. In the long run, this will be disruptive to daily functioning.
When the body’s natural circadian rhythm is disrupted, it places a good amount of stress on the body to function the way it is supposed to. This will result in a weakened immune system, making travelers susceptible to infections and illnesses.
Jet lag can lead to mental impairment such as difficulties with concentration, memory, and decision-making. Consequently, this leads to an increased risk of mistakes or accidents.
Frequent or chronic jet lag can have serious implications on health. It can lead to an increased risk of health conditions such as cardiovascular disease, obesity, and others.
Experiencing jet lag symptoms is not a very pleasant experience. I dread taking long-haul flights for that reason. Fortunately, there are many ways to if not prevent, reduce jet lag symptoms. Here are some tips on preventing and reducing jet lag symptoms.
Before your trip, you can try to adjust your sleep schedule such that you do not experience jet lag symptoms when you arrive at your destination. You may give yourself a few days to shift your bedtime and wake-up timings earlier.
Dehydration can contribute to the severity of jet lag. Thus, it is important that you ensure you are well-hydrated before, during, and after a flight.
Both caffeine and alcohol can interfere with your body’s ability to regulate sleep, which will lead to sleep disruption and worsening of jet lag symptoms. Try to avoid consuming these substances, especially when it is close to nighttime.
Light exposure is crucial to regulating your body’s internal clock. Some things you can do to get more light would be to expose yourself to any natural sunlight or use a light therapy device to reset your circadian rhythm.

If you want to avoid using sleep medicine or jet lag pills, you can opt to try natural supplements like melatonin at night to help you sleep better.

It is recommended that you consult a healthcare professional before starting on melatonin for the first time.
Jet lag recovery calculator is a tool that helps you to determine your optimal sleep and wake times based on your travel details. This will aid in a smoother transition to the new time zone and improve your well-being.
Lastly, you want to ensure that you are ShutEye®, to block out any disturbances that could be stopping you from a good night’s rest.
By implementing these strategies, you are sure to enjoy a smoother transition to a new time zone on your next flight.
In summary, while jet lag may be an unavoidable aspect of long-distance travel, you can minimize the impact by applying appropriate strategies. Adjusting your sleep schedule before a trip, creating a proper sleep environment, and staying hydrated all just a few of the many ways to manage jet lag and enjoy a smoother transition to your new destinations.
Remember, prioritizing rest is important even when you are traveling so try to be sure to bookmark these tips and beat jet lag!
Bon, O. L. (2018) Jet Lag. Circadian Rhythm - Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms. InTech. Available at: http://dx.doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.75929.
Choy, M., & Salbu, R. L. (2011). Jet lag: current and potential therapies. P & T : a peer-reviewed journal for formulary management, 36(4), 221–231. Suni, E. (2024) Jet Lag: Navigating Symptoms, Causes, & Prevention [online]. Available at: https://www.sleepfoundation.org/travel-and-sleep/jet-lag#references-78259