
Do you ever wake up unable to move, feeling a heavy weight on your chest, and sensing a presence in the room? You might be experiencing sleep paralysis, a perplexing phenomenon that affects many.
Discover the prevalence, triggers, and safety considerations associated with sleep paralysis. Finally, learn how to manage sleep paralysis episodes effectively.
Sleep paralysis is a common sleep disorder that occurs shortly after falling asleep or waking up. In this condition, individuals may suddenly wake up and find themselves unable to move or speak. Fortunately, recovery is quick, usually within a few seconds or minutes, allowing individuals to regain control of their bodies.

During an episode of sleep paralysis, your body experiences a temporary inability to move or speak, often accompanied by vivid hallucinations, such as sleep paralysis demon. This phenomenon occurs when your mind is awake, but your body remains in a state of muscle atonia, typical of REM sleep.
Seeking treatment for underlying conditions, improving sleep hygiene, and discussing your experiences with a healthcare professional are essential steps toward managing and potentially reducing the frequency of sleep paralysis episodes.
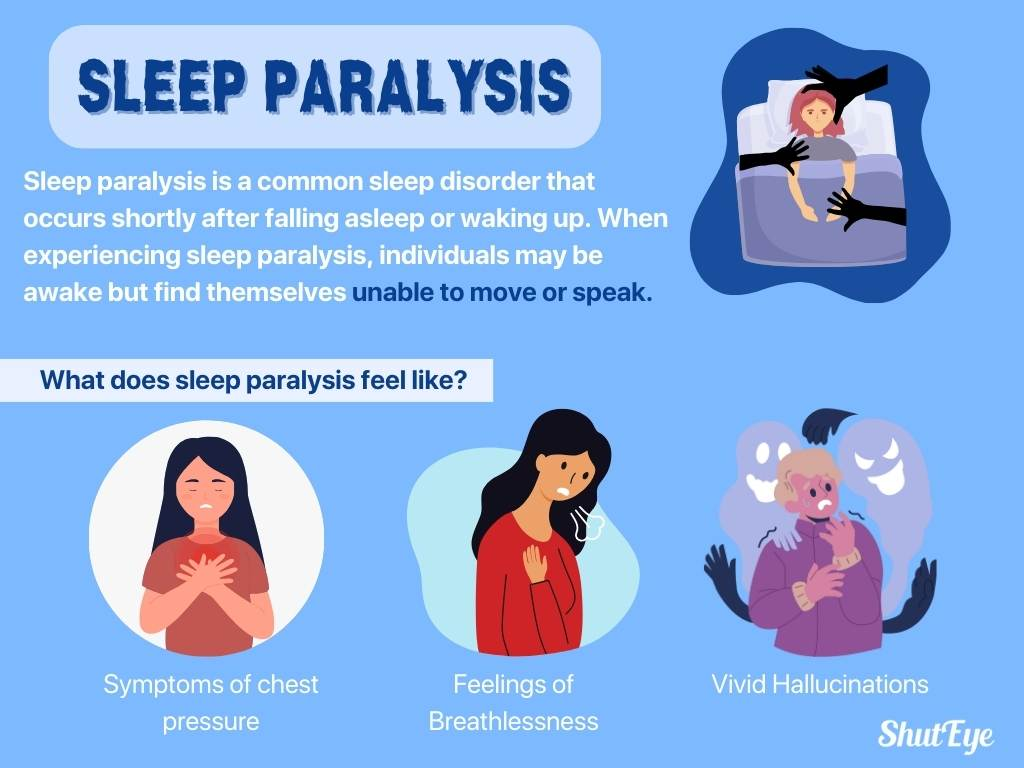
Experience sleep paralysis through a range of distressing symptoms and sensations. During sleep paralysis episodes, you may feel unable to move or speak, leading to feelings of fear and helplessness. Symptoms often include chest pressure, difficulty breathing, and intense emotions, followed by lingering fatigue.
Around 75% of cases involve vivid hallucinations, which can range from a sense of an intruder in the room to pressure on the chest. If you’re facing recurrent sleep paralysis, adopting good sleep hygiene practices like maintaining a regular sleep schedule and creating a comfortable sleep environment can help prevent future episodes.
Related content:
Turning Sleep Paralysis into a Lucid Dream
Explore the prevalence and causes of sleep paralysis to better understand this condition’s impact on individuals.
Sleep paralysis is a phenomenon of sleep that affects about 8% of the general population, with around 20% experiencing it in their lifetime. The cause of sleep paralysis isn’t precisely known, but factors like sleep disorders, mental health conditions, and family history are linked to its occurrence.
Traits such as imaginativeness and disassociation may also increase the likelihood of experiencing sleep paralysis. Recurring isolated sleep paralysis, where multiple episodes happen over time independently of other sleep disorders, is a common manifestation.
There are several factors that can contribute to sleep paralysis:
Understanding these factors can shed light on the complexities of sleep paralysis and its association with various sleep-related issues.
Delve into the association between sleep paralysis and sleep disorders, understanding their interplay and impact on individuals.
Understanding the connection between sleep paralysis and these sleep disorders can provide insights into potential triggers and help in developing effective treatment strategies to alleviate symptoms and improve sleep quality.

To safeguard your well-being and effectively address sleep paralysis, it’s crucial to consider safety measures and explore available treatment options.
While sleep paralysis is generally considered harmless, leading to emotional distress and sleep disruptions, understanding and addressing underlying conditions, such as narcolepsy, is vital. Adopting good sleep hygiene practices, including consistent routines, optimizing your sleep environment, and reducing substance use, can contribute to preventing episodes of sleep paralysis.
It’s pertinent to recognize and normalize your symptoms through consultation with a healthcare provider. Although there is no direct treatment for sleep paralysis during episodes, employing techniques like focusing on moving a small body part or adjusting breathing patterns may offer some relief.
Regarding the question of whether one can die from sleep paralysis, it’s important to clarify that sleep paralysis itself is not lethal. However, if you have concerns about your symptoms or if they are frequent and distressing, seeking professional help from a sleep specialist is recommended for further evaluation and management.
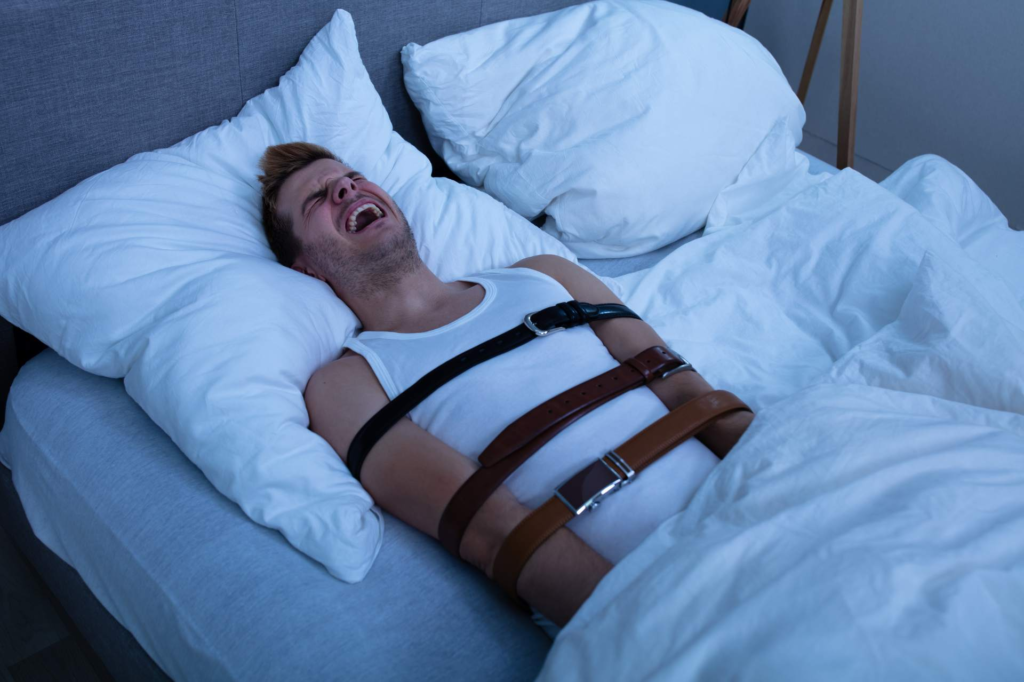

When experiencing sleep paralysis, you may encounter different types that vary in their characteristics and frequency. Here are the types to help you understand the phenomenon better:
These types can occur when falling asleep or waking from sleep and are associated with sudden waking from REM with relaxed muscles due to atonia. Symptoms include inability to move limbs, speak, and full awareness during episodes.
The exact cause of sleep paralysis remains unknown, but factors such as inadequate sleep, irregular sleep patterns, and stress are linked to its occurrence.
Explore the distinct characteristics of sleep paralysis to gain a deeper understanding of this phenomenon. When experiencing sleep paralysis, you may encounter isolated episodes, recurrent occurrences, or even recurrent isolated sleep paralysis (RISP). Below is a table highlighting the key characteristics of different types of sleep paralysis:
| Characteristics | Isolated Sleep Paralysis | Recurrent Isolated Sleep Paralysis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Occurs independently of other sleep disorders | Involves multiple episodes over time |
| Association with Other Issues | May not be linked to underlying sleep disorder | Ongoing instances without narcolepsy association |
| Potential Impacts | Can be an isolated event with no further recurrences | Involves repeated episodes without narcolepsy involvement |
Understanding these distinctions can aid in recognizing the nuances within the spectrum of sleep disorders, such as sleep apnea, and seeking appropriate treatment when necessary.
Transitioning from the characteristics of sleep paralysis, you can now delve into diagnosing and preventing episodes by understanding influencing factors and implementing proactive measures.
To effectively manage and support individuals experiencing sleep paralysis, you should focus on understanding their symptoms and seeking professional guidance. By improving sleep quality through implementing sleep hygiene techniques and seeking appropriate medical help, you can work towards resolving sleep paralysis episodes. Below is a table providing examples of sleep hygiene techniques that can assist in managing sleep paralysis:
| Sleep Hygiene Techniques | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Consistent Sleep Schedule | Regular bedtime and wake-up times | Enhances sleep quality and regulates body’s internal clock |
| Relaxing Bedtime Routine | Calming activities before sleep | Helps in winding down and preparing for restful sleep |
| Comfortable Sleep Environment | Optimal room conditions for sleep | Promotes relaxation and deep sleep |
Social Support
Behavior Management
Emotional Well-being
Monitoring Diary
Improving sleep quality and seeking professional guidance are essential for managing both narcolepsy and sleep paralysis effectively. When dealing with narcolepsy and its connection to sleep paralysis, remember these key points:

Related content:
Understanding the role of genetic predisposition in sleep paralysis can shed light on the potential hereditary factors influencing this parasomnia. Research suggests that a family history of sleep paralysis may increase the likelihood of experiencing this phenomenon.
While the exact genetic mechanisms are still being studied, there’s evidence to suggest that certain genetic factors could be linked to sleep paralysis. Individuals with a history of sleep paralysis and associated conditions within their families may be more prone to experiencing episodes themselves.
This genetic predisposition highlights the importance of exploring not only personal experiences but also the familial history of sleep-related issues when addressing and understanding sleep paralysis. By recognizing these potential genetic influences, individuals can better navigate their encounters with sleep paralysis.
In conclusion, sleep paralysis is a complex and unsettling phenomenon that can affect many individuals. By understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options, you can better navigate through episodes and improve your overall well-being.
Seeking professional help, improving sleep hygiene, and managing episodes effectively are key steps in addressing sleep paralysis. Remember, you aren’t alone in experiencing this mysterious aspect of sleep, and there are resources available to support you.
J Clin Med. (2023), Sleep Paralysis and Lucid Dreaming—Between Waking and Dreaming: A Review about Two Extraordinary States, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10218966/
Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2020), Prevalence and Clinical Picture of Sleep Paralysis in a Polish Student Sample, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7277803/
J Sleep Res. (2015), A twin and molecular genetics study of sleep paralysis and associated factors, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4950339/
Wróbel-Knybel P, Karakuła-Juchnowicz H, Flis M, Rog J, Hinton DE, Boguta P, Jalal B. Prevalence and Clinical Picture of Sleep Paralysis in a Polish Student Sample. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 May 18;17(10):3529. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17103529. PMID: 32443518; PMCID: PMC7277803.
Ableidinger S, Holzinger B. Sleep Paralysis and Lucid Dreaming-Between Waking and Dreaming: A Review about Two Extraordinary States. J Clin Med. 2023 May 12;12(10):3437. doi: 10.3390/jcm12103437. PMID: 37240545; PMCID: PMC10218966.
Olunu, E., Kimo, R., Onigbinde, E.O., Akpanobong, M.A.U., Enang, I.E., Osanakpo, M., Monday, I.T., Otohinoyi, D.A., & Fakoya A.O. (2018). Sleep paralysis, a medical condition with a diverse cultural interpretation. International Journal of Applied & Basic Medical Research, 8(3), 137–142. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30123741/
Denis, D., & Poerio, G. L. (2017). Terror and bliss? Commonalities and distinctions between sleep paralysis, lucid dreaming, and their associations with waking life experiences. Journal of Sleep Research, 26(1), 38–47. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27460633/
A.D.A.M. Medical Encyclopedia. (2021, April 19). Sleep paralysis. MedlinePlus., Retrieved June 6, 2023, from https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000801.htm